Figure 4. A subset of mt-tRNAs are affected by spurious 3’ adenylation in the absence of PDE12, leading to reduced aminoacylation of specific mt-tRNAs.
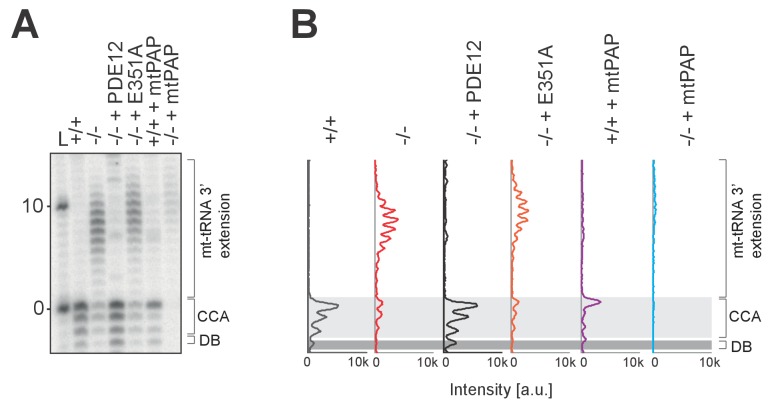
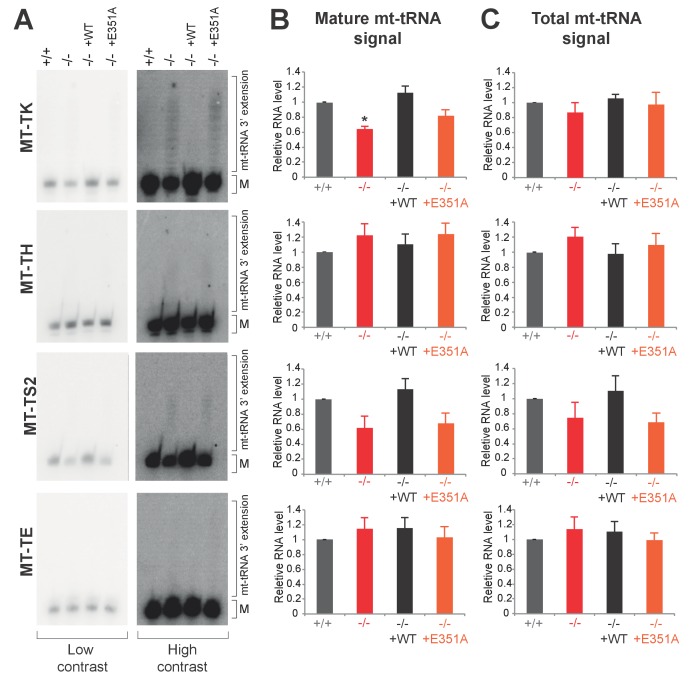
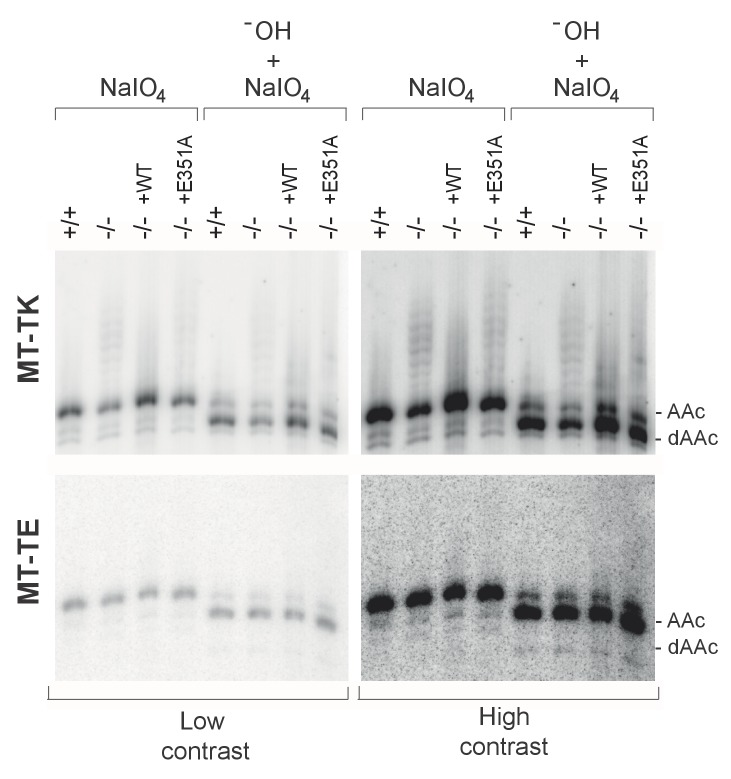
(A) Schematic of mt-tRNA structure depicting 3' extension determined via the radioactive MPAT (b) and MPAT-Seq (c). DB, discriminator base (B) Radioactive MPAT assay for a subset of mt-tRNAs extracted from PDE12+/+ and PDE12−/−. MPAT assay gel profiles were determined using ImageQuant. (C) Representation of 3’ ends of a subset of mt-tRNAs from PDE12+/+ and PDE12−/−, ascertained by MPAT-Seq. Read count shown for each position is relative to the read count for the corresponding discriminator base (DB) for each mt-tRNA. (D) Box-plot representation of percentage of mt-tRNAs molecules extended beyond the 3' CCA addition for all 22 mt-tRNAs, ascertained by MPAT-Seq, for PDE12+/+ and PDE12−/− cells, and in PDE12−/− cells expressing either wild-type PDE12 or E351A for 24 hr. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 with Student t-test relative to PDE12+/+. (p values: [+/+] vs. [−/−] p=0.0089, [+/+] vs. [−/− + WT] p=0.83, [+/+] vs [−/− + E351A] p=2.14×10−7). (E) Aminoacylation assay for subset of mt-tRNAs for PDE12+/+ and PDE12−/−. Profiles of aminoacylated mt-tRNAs were determined using ImageQuant. dAAc indicates intentionally deacylated samples.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27596.008