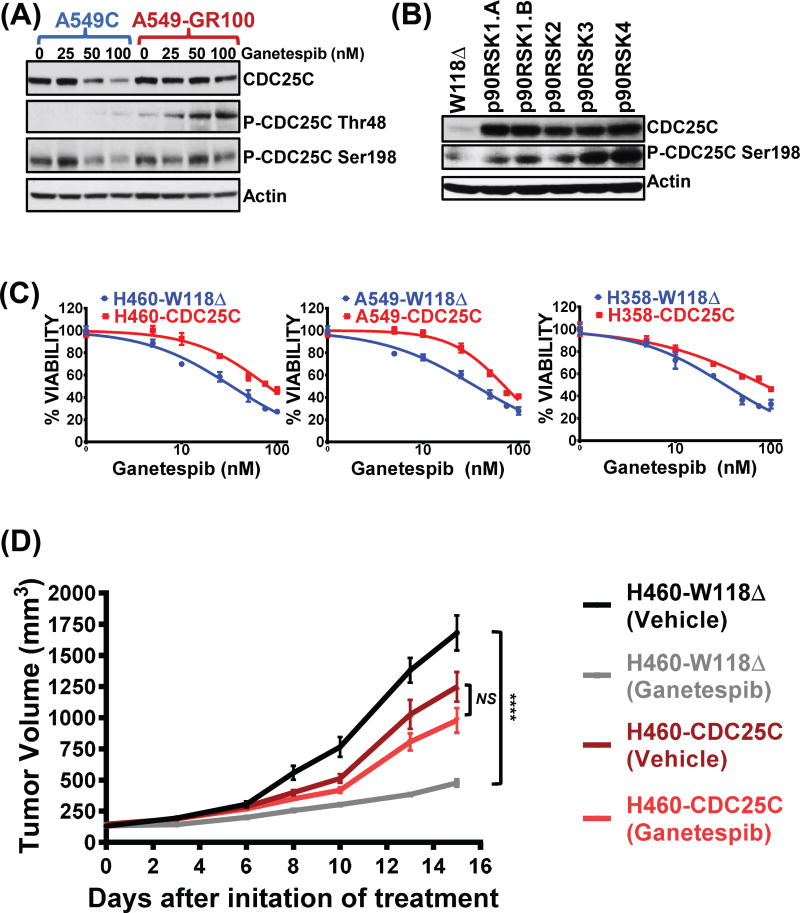
Figure 3. CDC25C, a p90RSK downstream target and an important inducer of G2/M progression, is hyperactivated in GR cells and its overexpression can lead to ganetespib resistance.
(A) Western blot analysis of the downstream p90RSK target, CDC25C, after ganetespib treatment (48 hours) in A549 C vs. GR cells. (B) Western blots showing overexpression of p90RSK isoforms leading to hyperactivation of CDC25C in parental A549 cells. (C) CDC25C was overexpressed in parental KRAS mutant NSCLC cell lines and percent viability were assessed by MTS assays after 72 hours treatment with increasing ganetespib doses. Cells expressing empty vector – W118Δ were used as a negative control. Unpaired t-test was performed on the IC50 values from three biological repeats to determine the level of significance and denoted as ***, p < 0.001. See Supplementary Table S3 for further details. (D) Ganetespib induced tumor regression was compared between vehicle and ganetespib treated H460 xenografts arms either overexpressing empty vector W118Δ or the CDC25C. Tumor growth curves represent mean tumor volume (± SEM). N = 9 mice per treatment arm. The two-tailed P value for H460-CDC25C (Vehicle) and H460-CDC25C (Ganetespib) was 0.1042, and considered not significant (NS). The two-tailed P value for H460-W118Δ (Vehicle) and H460-W118Δ (Ganetespib) was < 0.0001, and was considered extremely significant (****, p < 0.0001).