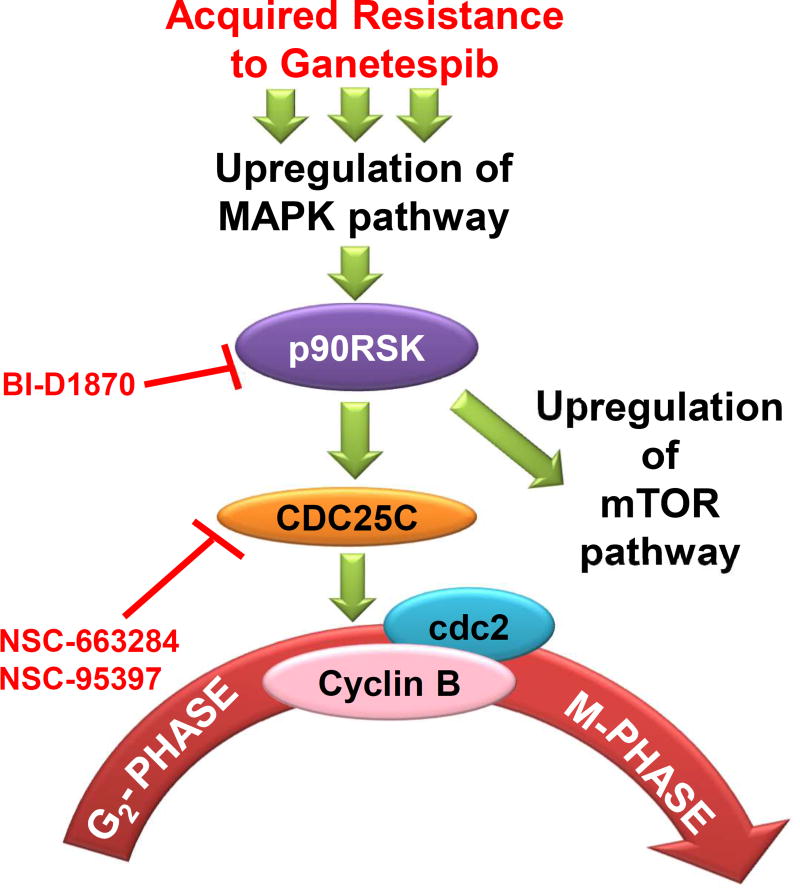
Figure 6. Acquired resistance to ganetespib in KRAS mutant NSCLC is mediated through bypass of ganetespib induced G2/M arrest in response to hyperactivation of p90RSK-CDC25C signaling pathway.
In KRAS mutant NSCLC, acquired resistance to ganetespib is initiated by hyperactivation of ERK, which in turn augments the expression of master switch, p90RSK. p90RSK hyperactivation then leads to hyperactivation of the mTOR pathways as well as induces G2/M progression via overexpressing and activation of CDC25C and subsequently its targets – Cyclin B1 and cdc2. Targeted inhibition of p90RSK or CDC25C induced synthetic lethality in GR cells. Based on these results, this model illustration proposes that combination of HSP90i, ganetespib with inhibitors of p90RSK (BI-D1870), or CDC25C (NSC-663284 or NSC-95397) may prevent ganetespib resistance and/or help overcome the resistance after single agent treatment.