Figure 1. Roles of Histone Chaperones in the Cell.
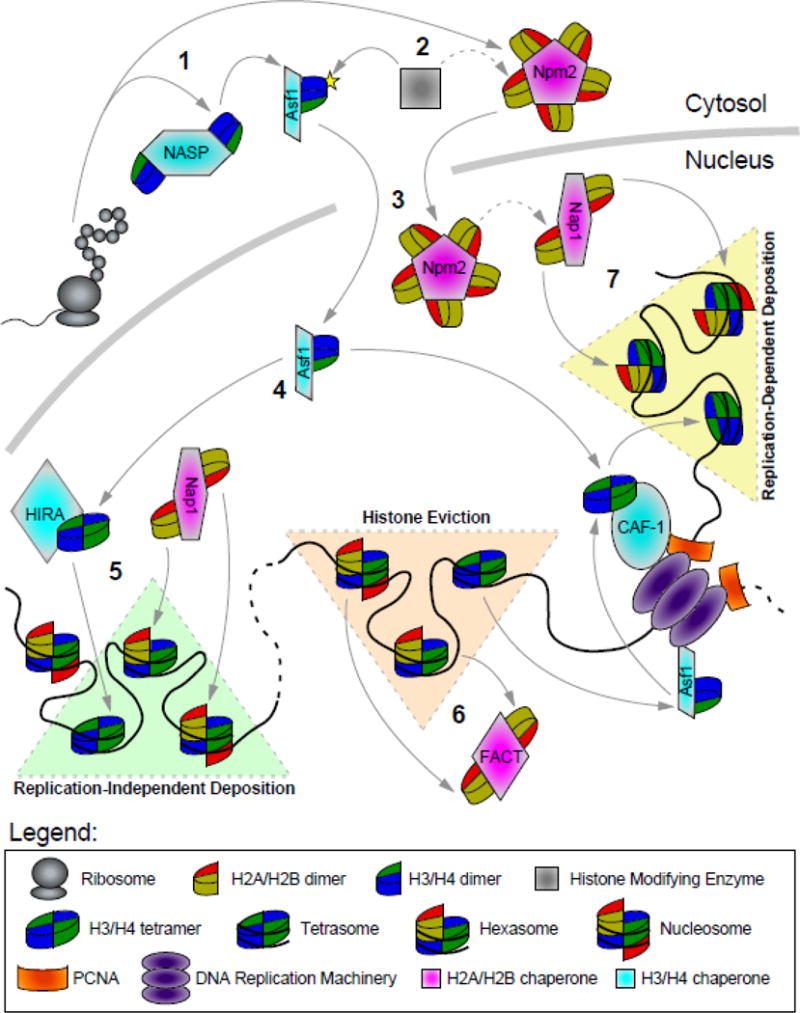
1. Heat-shock proteins (HSPs) along with histone chaperones, such as NASP, Npm2, and Asf1 bind to the newly translated histones and shield them from non-specific interactions in the cytosol.
2. Histone chaperones, such as Asf1 and RbAp46, provide a scaffold for pre-deposition histone modifications, such as HAT1-mediated acetylation of H4 tails. These modifications are crucial for nuclear import and transfer of H3/H4 to other chaperones. Less is known about the function of pre-deposition H2A/H2B modifications (dashed arrow).
3. Histone chaperones, such as Npm2, NASP, Nap1, and Asf1 use their nuclear localization signals (NLS) to interact with importins to aid in shuttling histones between the cytosol and nucleus. Histones also interact with import factors via NLS’s on their disordered tails. Chaperones also store and provide a soluble pool of histones.
4. Histone chaperones transfer histones to other chaperones. Asf1 transfers H3.1/H4 dimers to CAF-1 and H3.3/H4 dimers to HIRA, DAXX, or DEK for deposition. CAF-1 tetramerizes H3.1/H4 prior to deposition, whereas HIRA, DAXX and DEK may bind and deposit both the dimeric and tetrameric forms of H3.3/H4 depending on the chaperone bound and chromatin context (only the tetramer deposition model is shown for simplicity). Less is known about transfer among H2A/H2B chaperones (dashed arrow).
5. Replication-independent histone deposition of H3.3/H4 by HIRA, DAXX and DEK, and H2A/H2B by Nap1 and FACT. Histone variants can be incorporated by other variant-specific histone chaperones, such as YL1, HJURP and APLF.
6. Chaperones, along with ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers, mediate histone eviction prior to DNA replication. H2A/H2B is displaced by FACT and Nap1. H3/H4 is displaced by Asf1 and recycled by CAF-1. Large-scale histone eviction occurs during DNA replication (shown), transcription, and DNA repair. The MCM2 subunit of the replisome aids in Asf1-mediated chaperoning at the replication fork, and CAF1 also interacts with the sliding clamp PCNA. Histone variants can be displaced by variant-specific chaperones, such as ANP32E and ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers such as SWR1.
7. Replication-dependent histone deposition of H3.1/H4 by CAF1 and H2A/H2B by Nap1.
