Figure 6.
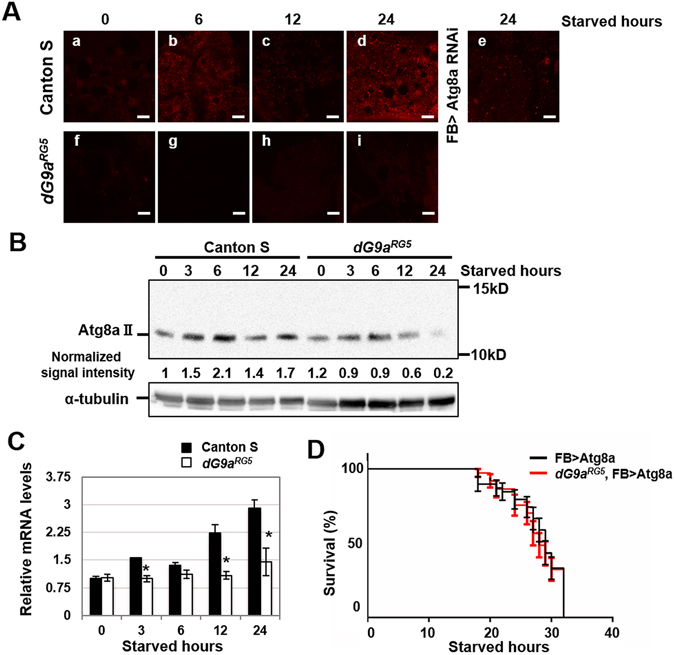
dG9a is responsible for the induction of autophagy under starvation stress. (A) Immunostaining of wild-type and dG9aRG5 mutant fat bodies under starvation conditions with an anti-Atg8a antibody. Strains: (a–d) Canton S (e) w; FB-GAL4/+; Atg8aHMS01328/+ (f–i) dG9aRG5. Starved hours: (a,f) 0 h (b,g) 6 h (c,h) 12 h (d,i) 24 h. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) A western blot analysis of extracts from the starved wild-type and dG9aRG5 mutant. Blots were probed with anti-Atg8a and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. Signal intensity normalized with that of α-tubulin is shown. The full-length image of the blot is shown in Fig. S6B. (C) Quantification of mRNA levels by a RT-qPCR analysis of Atg8a in the starved wild-type and dG9aRG5 mutant. Results were normalized to α-tubulin and displayed as relative values to that of the 0-h starved wild-type n = 3. *P < 0.05. (D) The results of a viability assay under starvation conditions using the males of dG9aRG5, FB > Atg8a (dG9aRG5; FB-GAL4/Atg8aScer/UAS.P/T.T:Avic/GFP-EGFP,T:Disc/RFP-mCherry; +) (n = 39 from 2 independent experiments) and FB > Atg8a (+; FB-GAL4/Atg8aScer/UAS.P/T.T:Avic/GFP-EGFP,T:Disc/RFP-mCherry; +) (n = 38 from 2 independent experiments) strains P = 0.79. (C,D) Error bars represent SE.
