Figure 1.
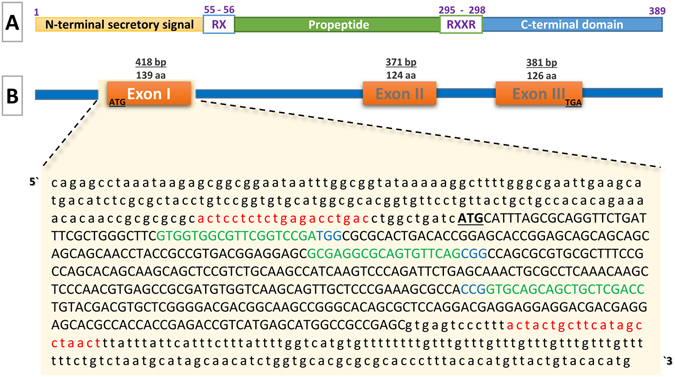
Design of the CRISPR/Cas9 system. (A) Schematic diagram of channel catfish MSTN; a signal sequence (N-terminal secretory signal), a propeptide domain (propeptide) and a bioactive domain (C-terminal domain). RX (55–56) is a proteolytic site to remove the signal sequence and RXXR (295–298) is a proteolytic processing site (RSSR) to produce C- terminal bioactive form of MSTN. These 3 domains (389 amino acids) are encoded from (B) the three exons of the channel catfish MSTN gene; Exons I, II and III consist of 418, 371 and 381 base-pairs encoding 139, 124 and 129 amino acids residues, respectively. CRISPR/Cas9 target sites in Exon I; The Exon and Introns are indicated by upper and lower case, the underlined Bold uppercase are the start and stop codons, The primers used in PCR are indicated in red, The guide RNA target sites are indicated in green followed by PAM (Protospacer adjacent motif, NGG) in Blue.
