Figure 1.
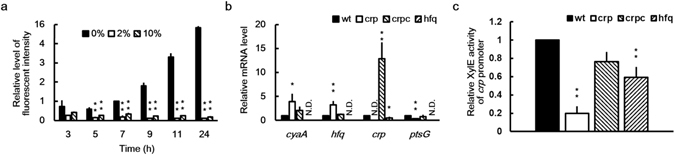
Crp activity was inhibited by high glucose levels; cyaA, hfq, ptsG, and crp itself were regulated by Crp, and crp was regulated by Hfq in P. mirabilis. (a) Crp activity increased in the absence of glucose and decreased by 2% and 10% (2000 and 10,000 mg/dL) glucose. The plac-gfpuv reporter plasmid-transformed wild-type P. mirabilis was grown in LB broth with or without glucose, and the fluorescent intensity of GFPuv was monitored after incubation for 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 24 h. The fluorescent intensity in the absence of glucose at 7 h was set at 1, and all other data are expressed relative to this value after being normalized against the OD600 value. The data are the averages and standard deviations of three independent experiments. The significant difference between the presence and absence of glucose at each time point was determined using the Student’s t test (**P < 0.01). (b) Crp regulated the expression of cyaA, hfq, and ptsG mRNA, and crp expression was regulated by Hfq in P. mirabilis. Overnight bacterial cultures were diluted in LB broth and incubated for 7 h before total RNA was prepared for measuring mRNA levels of cyaA, hfq, crp, and ptsG in the wild-type strain, crp mutant, crp-complemented strain, or hfq mutant by using real-time RT-PCR. The mRNA level for the wild-type strain was set at 1, and all other data are expressed relative to this value. N.D., not determined. (c) crp promoter activities of wild-type P. mirabilis, crp mutant, crp-complemented strain, and hfq mutant. The activities of XylE in the crp-xylE reporter plasmid-transformed P. mirabilis strains were determined using the reporter assay at 7 h after incubation. The value obtained for the wild-type strain was set at 1. In (b) and (c), the data are the averages and standard deviations of three independent experiments. Significant difference from the wild-type strain is indicated with an asterisk (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 by using Student’s t test). wt, wild-type; crp, crp mutant; crpc, crp-complemented strain; hfq, hfq mutant.
