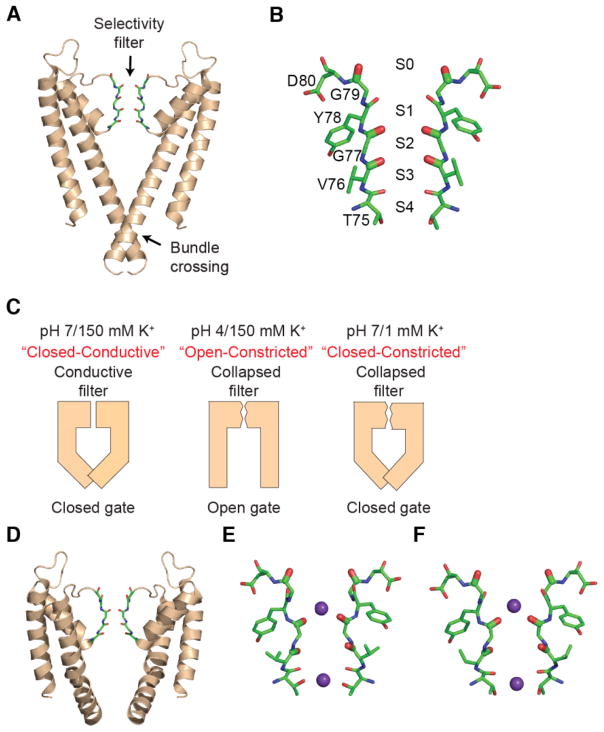
Fig. 1. Structures of KcsA with constricted selectivity filter and open or closed intracellular gates.
(A) Structure of the wild-type KcsA channel (pdb: 1K4C). Two opposite subunits of the tetrameric channel are shown. The selectivity filter (sticks) and the intracellular bundle crossing of the channel are indicated. (B) The backbone carbonyls of residues Thr75 to Gly79 line the selectivity filter and comprise the four ion binding sites (denoted S1 to S4). (C) Different experimental conditions modulate the conformations of the selectivity filter and intracellular gate. At pH 7 and 150 mM K+, the selectivity filter is in a conductive conformation and the bundle crossing gate is closed. At pH 4 and 150 mM K+, the selectivity filter is constricted and the gate open. Similarly, at pH 7 and 1 mM K+, the selectivity filter is constricted and the gate closed. (D) Structure of KcsA in the open-constricted state (pdb: 3F5W). (E) Selectivity filter of KcsA in the open-constricted state (pdb: 3F5W). (F) Selectivity filter of KcsA in the closed-constricted state (pdb: 1K4D).