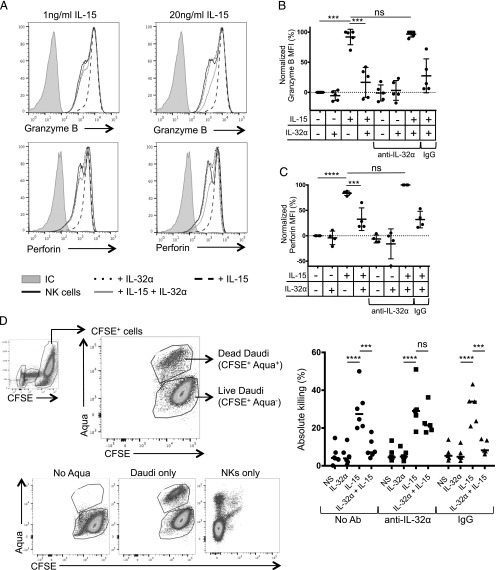
FIGURE 3.
IL-32α controls NK cell effector molecule expression. (A) NK cells were isolated from human PBMCs and incubated overnight with IL-32α (100 ng/ml), IL-15 (1 or 20 ng/ml), or both cytokines. The production of granzyme B and perforin was assessed by flow cytometry. Histograms show the expression of granzyme B and perforin in NK cells upon exposure to the different cytokines. (B) Graph shows granzyme B expression in at least four experiments. A neutralizing anti-32α Ab or an isotype-matched control (rabbit polyclonal) was added where indicated. Results were normalized to nonstimulated cells and plotted as a normalized mean fluorescence intensity. The level of granzyme B and perforin that was induced following IL-15 stimulation was set at 100%, whereas the expression of granzyme B and perforin in unstimulated NK cells was set at 0%. IL-32α was used at 100 ng/ml, and IL-15 was used at 1 ng/ml; each dot represents one experiment. Values are shown as average ± SD. (C) Similar to (B), graph shows perforin expression in at least four experiments. (D) Isolated NK cells were stimulated with IL-32α (100 ng/ml), IL-15 (1 ng/ml), and IL-32α + IL-15, and cocultured with CFSE-labeled Daudi cells. Dot plots show the gating strategy to assess percentage of live and dead CFSE+ Daudi cells. Graph shows the absolute killing by NK cells stimulated with IL-32α, IL-15, and IL-32α + IL-15 in absence or presence of anti–IL-32α neutralizing Ab or an isotype-matched control (rabbit polyclonal). Values are calculated as average ± SD. ***p ≤ 0.005, ****p ≤ 0.001. NS, nonstimulated; ns, not significant.