Figure 3.
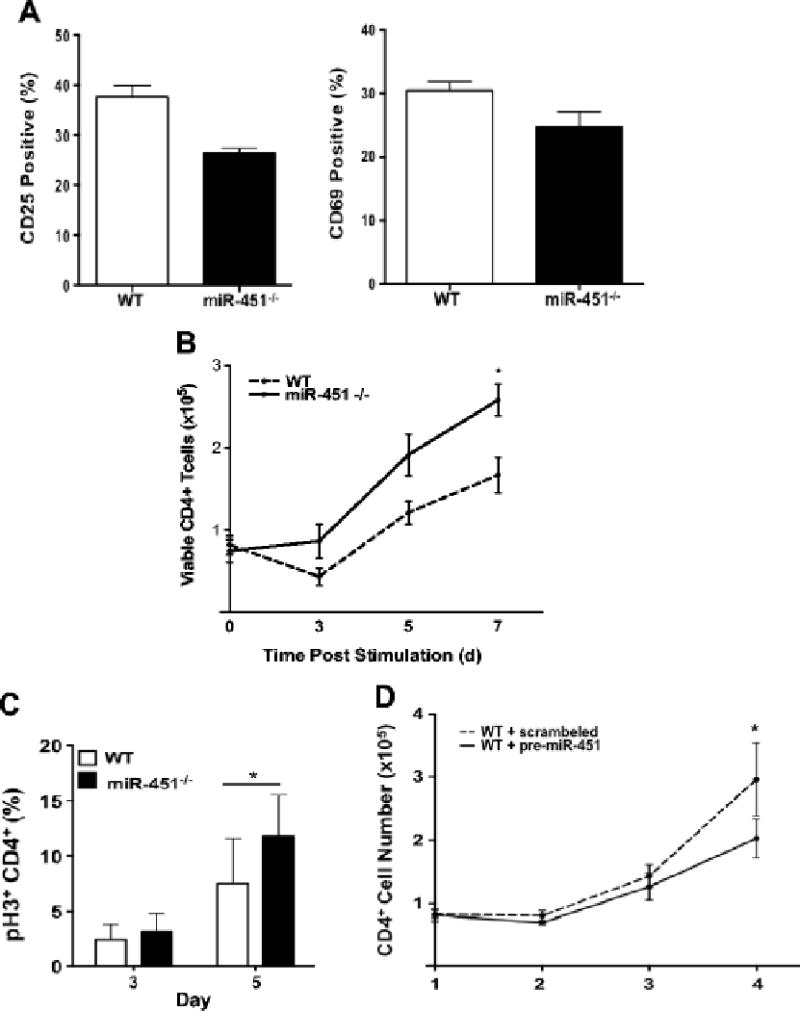
miR-451 inhibits CD4+ T-cell proliferation in vitro. a) WT and miR-451−/− CD4+ cells have similar activation. WT and miR-451−/− CD4+ cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and CD28 antibodies and CD25 and CD69 expression determined 48 hrs later (mean ± S.E.M., N=4). b–c) miR-451−/− CD4+ T cells have increased proliferation. CD4+ cells from WT and miR-451−/− mice were stimulated and b) cell numbers (mean ± S.E.M., N=8, *P<0.05, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test) and c) pH3 as a marker of active cell cycle by flow cytometry was determined on multiple days (mean ± S.E.M., N=4, Students t-test, *P<0.05). d) Increased miR-451 decreases CD4+ T-cell proliferation. CD4+ cells were treated with miR-451 pre-miRNA or a scrambled control and co-stimulated. Cell numbers were determined (mean ± S.E.M., N=4, *p<0.05, paired t-test).
