Figure 4.
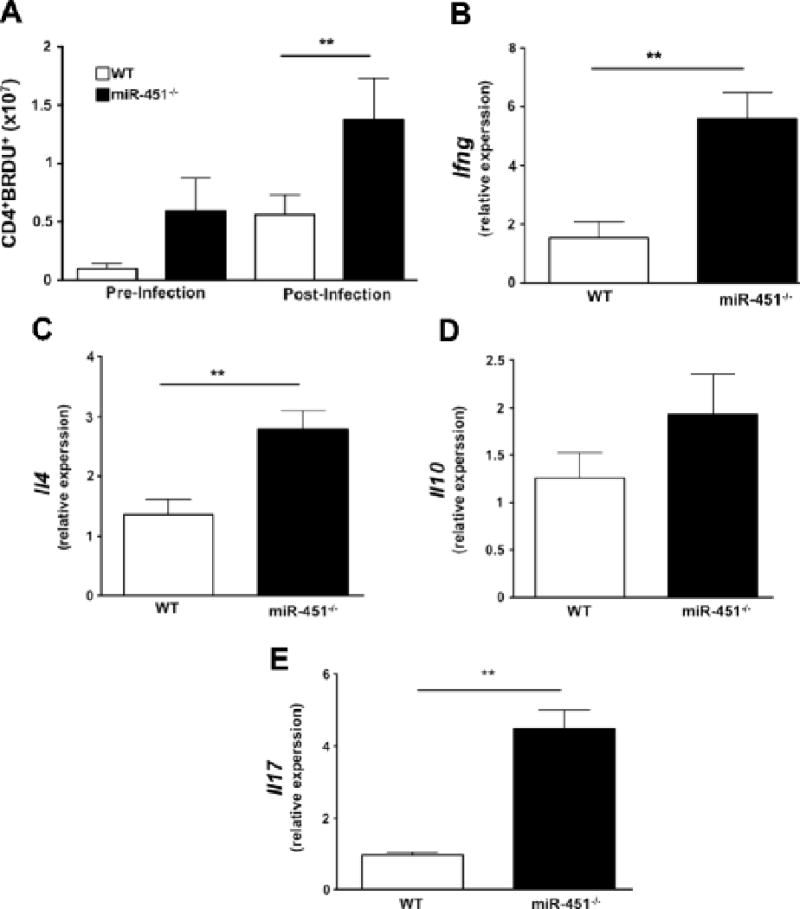
a) Mice lacking miR-451 have more in vivo CD4+ T-cell proliferation both pre- and post- infection as determined by the number of BRDU+ CD4+ cells (mean ± S.E.M., N=4-5 pre and N=8 post infection, **p<0.01, representative of 2 independent experiments). b–e) miR-451−/− T cells have increased cytokines post infection. mRNA was isolated from WT and miR-451−/− T cells on day 9 postinfection and qRT-PCR performed for Ifng, Il4, Il10 and Il17. Ifng, Il4, and Il17, but not Il10, were significantly increased in T cells from miR-451−/− mice (mean ± S.E.M., N= 3-4, **p<0.01, relative to Tbs and Rna18s5).
