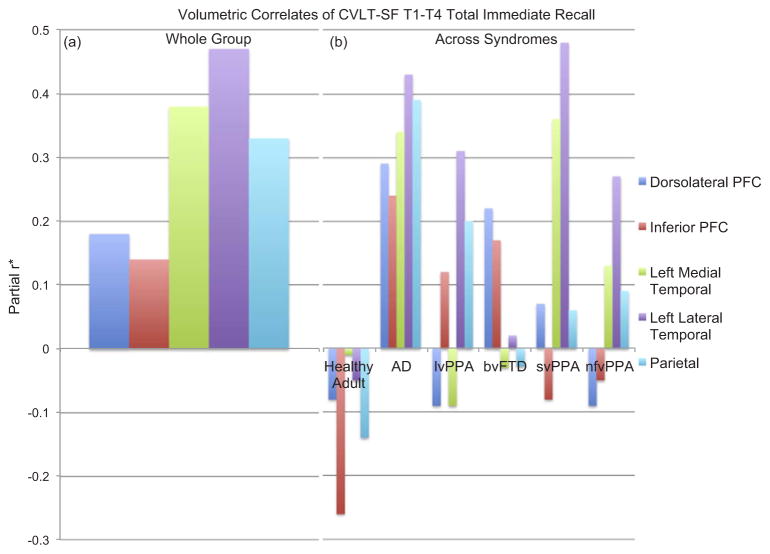
Fig. 4.
Distinct neuroanatomic correlates are associated with CVLT-SF T1-T4 Total Immediate Recall Performances both within (a) and across (b) diagnostic groups. Note. (a) The neural correlates of immediate recall are also multifaceted, though demonstrating the largest associations with temporal-parietal regions. (b) However, these neuroanatomic patterns vary highly depending on the clinical syndrome examined; for example, in AD, a largely dispersed pattern of anatomic regions is evidenced, whereas in bvFTD, only frontal regions are associated with immediate recall performances. *Partial r adjusted for age, sex, and total intracranial volumes; CVLT-SF T1-T4 = California Verbal Learning Test – short form Trials 1–4; AD = Alzheimer’s disease; lvPPA = logopenic variant primary progressive aphasia; bvFTD = behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia; svPPA = semantic variant primary progressive aphasia; nfvPPA = nonfluent variant primary progressive aphasia.