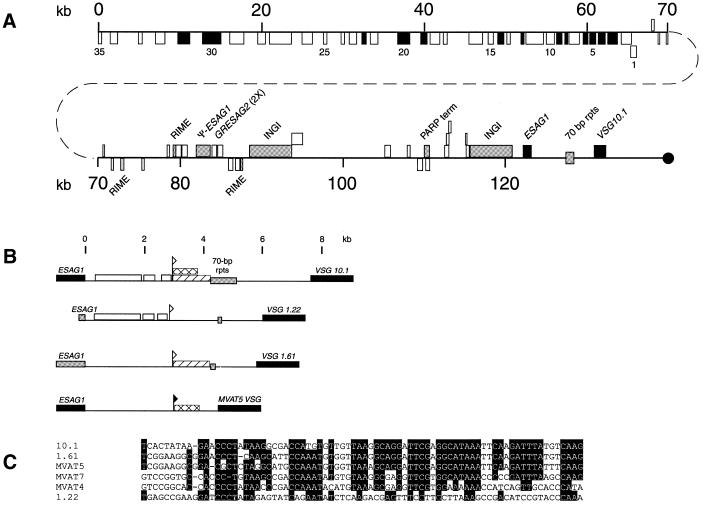
Figure 3.
Gene organization of the VSG 10.1 donor copy. (A) The location and coding strand of the genes and repeat elements in BAC clone 45I2 are indicated by boxes. Genes or repeat elements shown above the line are located on the ‘top’ strand and are oriented towards the telomere (black circle), whereas those shown below the line are located on the ‘bottom’ strand and oriented away from the telomere. Black boxes indicate known genes and genes with significant homology to known genes (see Table 1). White boxes designate hypothetical genes with no significant homology to known genes. Numbers 1–35 refer to the 35 adjacent ORFs oriented away from the telomere. Gray boxes specify repeat elements (RIME, INGI and 70 bp repeats), pseudo genes, and a PARP transcription terminator. The region beginning in the 70 bp repeats and extending through VSG 10.1 has been duplicated in the GUTat 10.1 B-ES. (B) Comparison of the putative VSG 10.1 M-ES to the M-ESs of VSG 1.22, VSG 1.61 and MVAT5 VSG. Regions in the putative VSG 10.1 M-ES with >80% sequence identity to other M-ESs are indicated (VSG 1.22, white box; VSG 1.61, diagonal lined box; MVAT5 VSG, crosshatched box). The MVAT5 promoter is indicated by a closed flag. Sequences within the VSG 10.1, VSG 1.22 and VSG 1.61 M-ESs that have homology to the MVAT5 promoter are marked by an open flag. Black boxes indicate ESAG 1 and VSG genes. Gray boxes indicate pseudo-ESAG 1 genes and 70 bp repeats. (C) Nucleotide sequence comparison of the MVAT4, 5 and 7 M-ES promoters to sequences from the VSG 10.1, VSG 1.22 and VSG 1.61 M-ESs. Shaded residues are conserved in at least four of the six sequences shown.