Figure 7. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium longum treatment on the systemic inflammatory response.
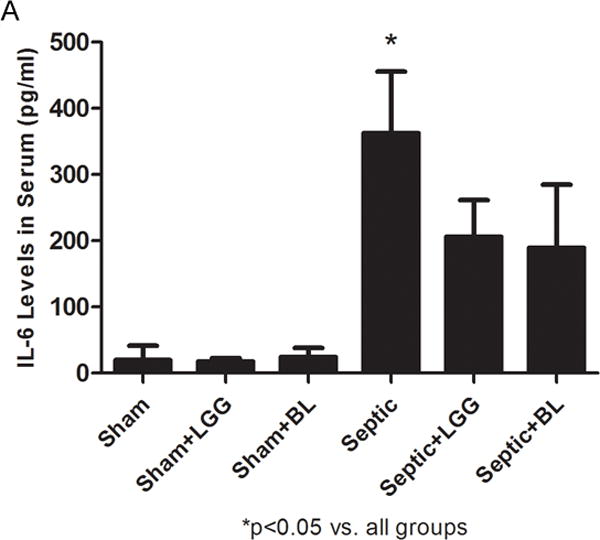
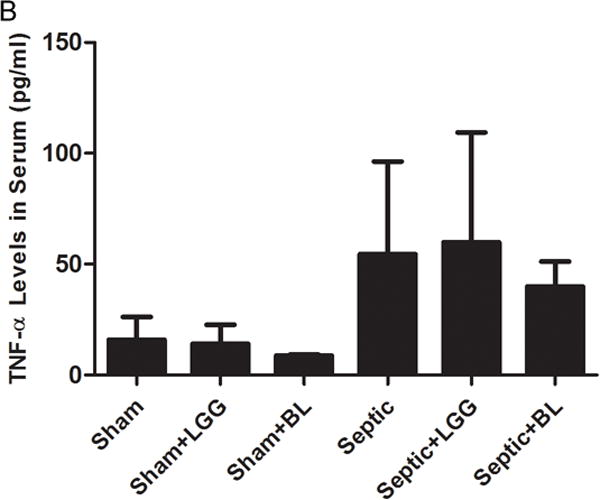
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to determine the concentrations of TNF-α and IL-6 in serum. (A) IL-6 was significantly elevated in the serum of septic mice compared to shams (septic 383.5 ± 93.1 vs. shams 19.8 ± 21.4, p = 0.0001), while treatment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) or Bifidobacterium longum (BL) in septic mice led to significantly reduced systemic IL-6 levels (LGG 206.1 ± 55.2 vs. septic 383.5 ± 93.1, p = 0.0075 and BL 189.4 ± 95.2 vs. septic 383.5 ± 93.1, p = 0.0069) compared to septic mice not treated with probiotics. (B) There were no differences between groups for TNF-α in the serum. Shams n = 5 per group; Septic n = 7; LGG n = 5; BL n = 6. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD.
