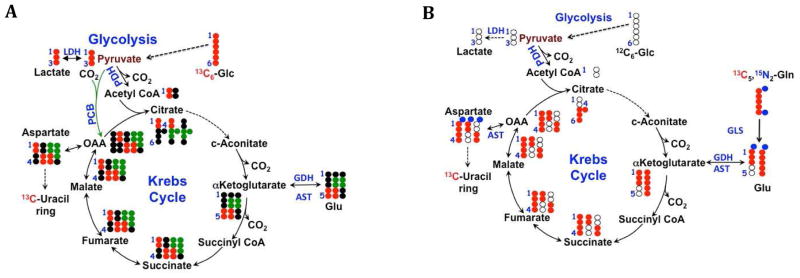
Figure 2. Glu isotopomers from Krebs cycling.
Isotopomers created via Krebs cycle activity by: (A) 13C6 glucose. Black dots are 12C. 13C6 glucose (red dots) produces 13C3 pyruvate which can enter the Krebs cycle either via PDH (2 13C) or PCB (3 13C, shown as green dots), which give rise to different isotopomers of Krebs cycle intermediates and anabolic products such as uracil and its precursor Asp, distinguishable by NMR as 13C1,2 + 13C3,4 via PDH in the forward direction, and 13C1,2,3 Asp via PCB (B) 13C5,15N2 Gln plus unlabeled glucose. Red dots are 13C atoms from Gln, blue dots are the two nitrogen atoms. Open circles are 12C. The anaplerotic input of fully labeled Gln produces the fully labeled Krebs cycle intermediates. Fully labeled OAA from Gln condenses with glucose-derived AcCoA to produce quadruple labeled citrate, which becomes via the Krebs cycle triply labeled αKG, and doubly labeled succinate. AST will transaminate OAA with Glu, transferring the amino nitrogen to Asp. The isotopomers produced evolve on further cycles, and differ with other inputs to the cycle. Isotopomer analysis is needed to sort out the resulting complex patterns.