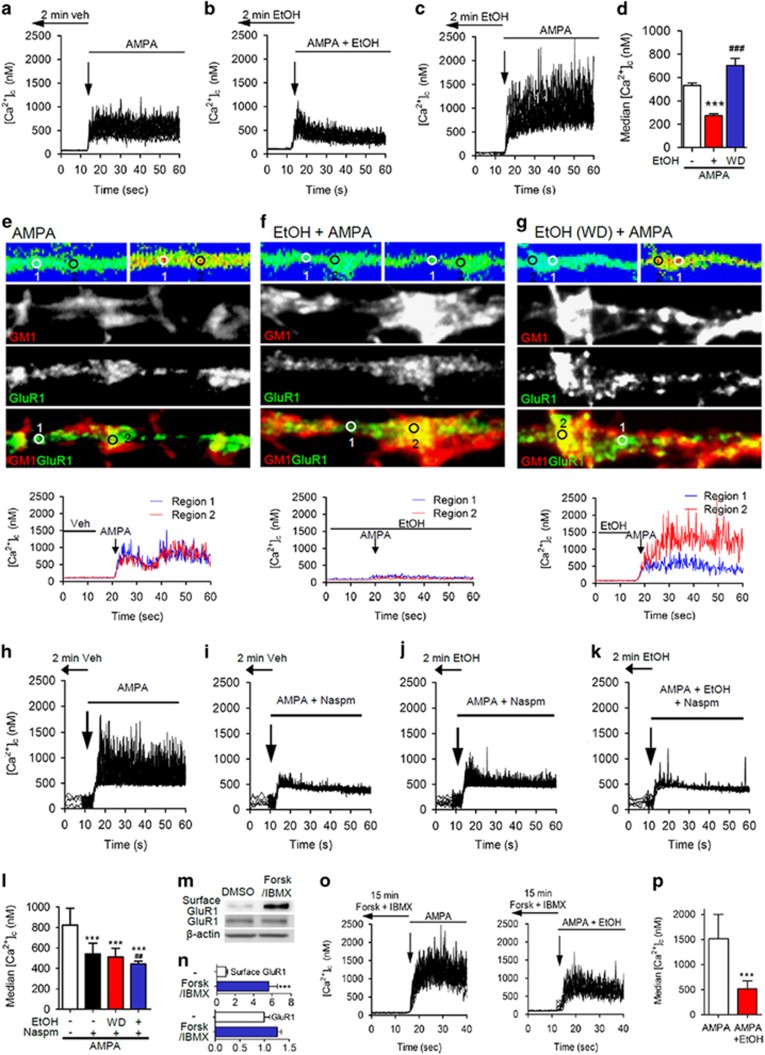
Figure 4.
Sensitization of focal AMPA-evoked calcium responses in membrane microdomains. AMPA-evoked calcium transients were measured along dendritic branches using the ratiometric calcium probe Fura-2 at the rate of 10 image pairs per second. Focal calcium bursts evoked by (a) AMPA (20 μM) were (b) suppressed when EtOH remained present in the bathing media, and (c) enhanced during EtOH WD. (d) Quantitation of AMPA-evoked calcium transients showing the median amplitudes of calcium responses for the indicated conditions. (e–g) Representative images for the indicated conditions showing (from top to bottom) pseudocolor images of baseline and AMPA-evoked calcium transients, immunofluorescent staining of the same dendrite for GM1, GluR1 and the merged images. Lower tracings show baseline and AMPA-evoked calcium responses for the indicated regions. (h–k) Representative traces of AMPA-evoked calcium transients evoked after a 2 min pre-exposure to vehicle or EtOH were inhibited by the selective calcium-permeable AMPAR antagonist, Naspm trihydrochloride (Naspm, 50 μM). (l) Quantification of AMPA-evoked calcium transients showing the median amplitudes of calcium currents evoked under the indicated conditions. (m) Representative immunoblots of rat hippocampal neurons treated with forskolin (Forsk, 20 μM) and IBMX (50 μM). (n) Quantification of surface GluR1 and total GluR1 after treatment of forskolin and IBMX. (o) Representative traces of AMPA-evoked calcium responses in neurons pretreated with forskolin and IBMX and then continuously exposed to EtOH. (p) Quantification of AMPA-evoked calcium responses for the indicated conditions. Data are median±s.d. ***P<0.001; ##P<0.01; ###P<0.001. AMPA, n-2-amino-3-(5-methyl-3-oxo-1,2-oxazol-4-yl) propanoic acid; AMPAR, AMPA receptor; EtOH, ethanol; IBMX, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine; WD, withdrawal.