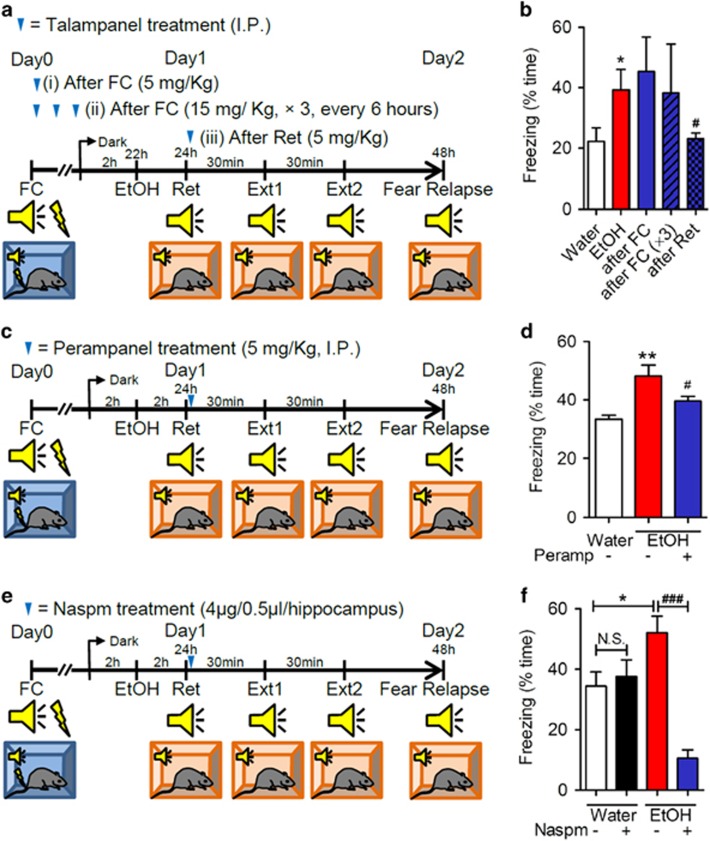
Figure 5.
AMPAR antagonists rescue EtOH-associated impairment in the consolidation of extinction. (a) Schematic illustration of therapeutic time windows for Talampanel administration. Talampanel was intraperitoneally injected immediately following fear conditioning (i, 5 mg kg−1), three times over 18 h (ii, 6 h interval, 5 mg kg−1), or a single dose after retrieval (iii, 5 mg kg−1). Blue arrows depict dosing time and intervals. (b) Quantitative data showing freezing (% time) during fear relapse testing for the indicated treatment conditions. (c) Schematic illustration of timing for Peramapanel treatment. A single dose of Perampanel was intraperitoneally injected after retrieval (blue arrow, 5 mg kg−1). (d) Quantitative analysis of freezing behavior (% time) for the indicated treatment conditions. (e) Schematic illustration of timing for Naspm treatment. Mice received bilateral injections of Naspm into hippocampi (4 μg per 0.5 μl per min) after exposure to the retrieval cue. (f) Quantitative analysis of freezing behavior (% time) for the indicated treatment conditions. Data are mean±s.d. of n=10–14 animals per condition. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, #P<0.05 and ###P<0.001. ANOVA with Tukey post hoc comparisons. ANOVA, analysis of variance; AMPA, n-2-amino-3-(5-methyl-3-oxo-1,2-oxazol-4-yl) propanoic acid; AMPAR, AMPA receptor; EtOH, ethanol; FC, fear conditioning.