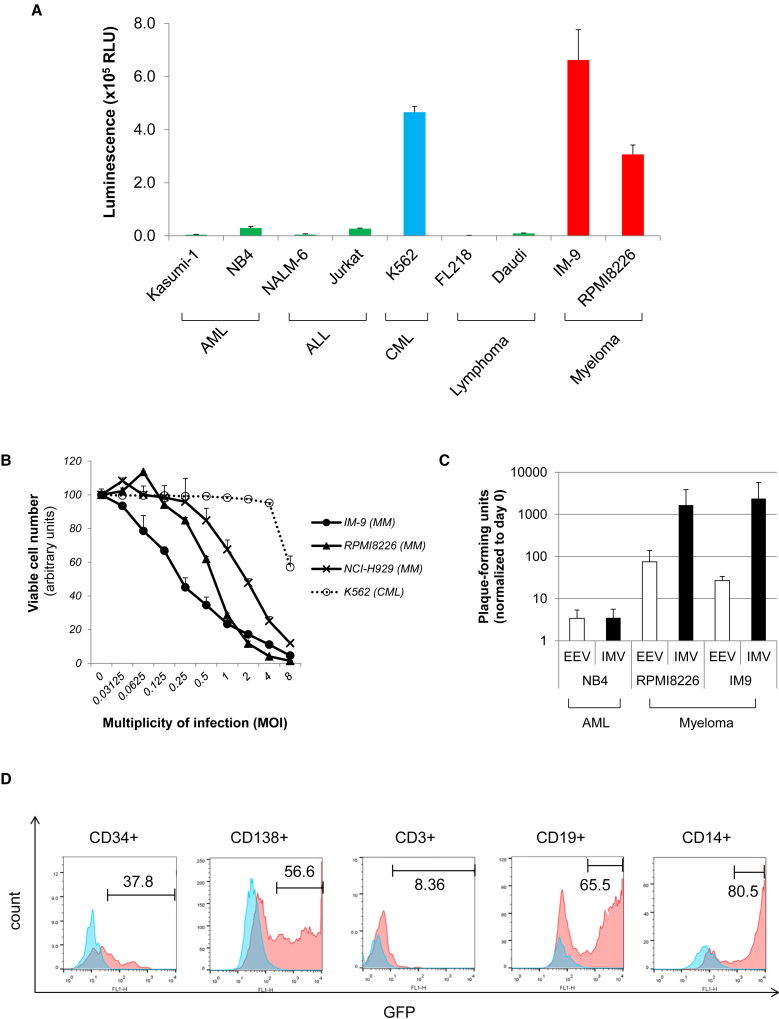
Figure 1.
Myeloma Cells Are Sensitive to VV
(A) Infectivity of leukemia/myeloma cell lines to VV. Cell lines derived from acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), malignant lymphoma, and multiple myeloma were infected with a firefly-luciferase-expressing VV (LC16m8Δ-B5R-FlucIRESgfp) at an MOI of 1. Luciferase activity was determined at 12 hr after infection. Data represent the means and SD of three independent experiments. (B) Cell viability after infection. Cells (1 × 104/well) were seeded in 96-well plates and cultured for 72 hr in the absence or presence of different concentrations of the VV strain LC16m8Δ-B5R-FlucIRESgfp (MOIs = 0–8). The number of viable cells was determined using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo). Data represent the mean and SD of three independent experiments. (C) Cells were infected with LC16m8Δ-B5Rgfp at an MOI of 0.1. Extracellular enveloped virus (EEV) and intracellular mature virus (IMV) were collected from supernatant and cell pellet at 72 hr after infection. Harvested virus was titrated by the infection to RK13 cells. Data represent the means and SD of three independent experiments. (D) Infectivity of myeloma patient bone marrow cells. Bone marrow mononuclear cells derived from a myeloma patient were infected with LC16m8Δ-B5Rgfp at an MOI of 1 and cultured for 48 hr. The frequency of virus-infected cells (GFP+) was compared among CD34+ cells (hematopoietic progenitors), CD138+ cells (myeloma), CD3+ cells (T lymphocytes), CD19+ cells (B lymphocytes), and CD14+ cells (monocytes). Histograms of non-infected cells (blue) are overlaid with infected cells (red).