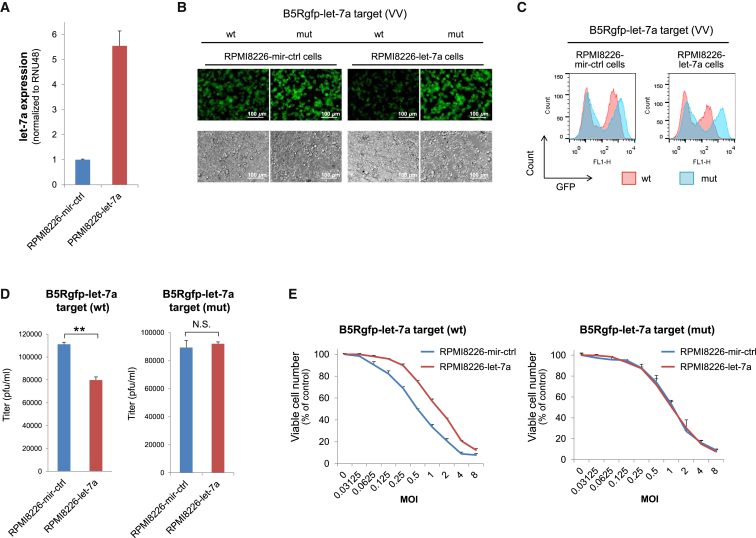
Figure 4.
Let-7a Overexpression Inhibits VV Infectivity
(A) qRT-PCR analysis of let-7a. RNA was extracted from RPMI8226 cells lentivirally transduced with miR-ctrl or let-7a. The RNA expression was normalized to that of the endogenous control RNU48. (B) In vitro infection with let-7a-regulated VVs. Cells were infected with each VV at an MOI of 1 and cultured for 48 hr. (C) Flow cytometric analysis. GFP expression by the VV containing wild-type let-7a-target or the mutated let-s7a-target is shown in red or blue, respectively. (D) Replication of VVs. Cells (1 × 104/well) were infected with VVs with either the wild-type or mutated let-7a-target at an MOI of 0.1 and grown in 96-well plates. Viruses were collected from the infected cells 72 hr after infection. Harvested viruses were titrated via infection of RK13 cells. **p < 0.01 (Student’s t test). (E) Cell viability after infection. Cells (1 × 104/well) were seeded in 96-well plates and cultured for 72 hr in the absence or presence of different concentrations of the VVs containing either the wild-type or mutated let-7a-target (MOI = 0–8). The number of viable cells was determined using the Cell Counting Kit-8. The error bars represent the SDs of three independent experiments. mut, mutated; WT, wild-type.