Table 1.
Glycosylation Reactions
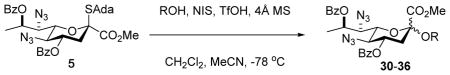
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Acceptor | Product | % Yield, α:β ratio | 3JCH (Hz) |
| 1 | BnOH |
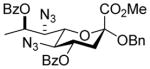 30 |
96%, α-only | 30: 7.2 |
| 2 |
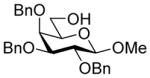 27 |
31αβ |
87%, 6.7:1 | 31α: 6.4 |
| 3 |
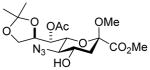 26 |
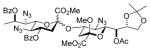 32α,β |
82%, 4.4:1 | 32α: 6.9 |
| 4 |
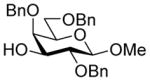 28 |
33α,β |
75%, a4.5:1 |
33α: 7.2 33β: 0 |
| 5 |
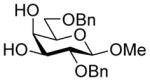 29 |
34α,β |
88%, 34α:34β:35α= 4.7:1:0.9 | 34α: 7.0 |
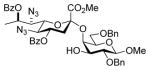 35 |
35α: 6,3 | |||
| 6 | 1-adamantanol |
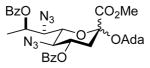 36α,β |
73%, 4.2:1 | 36α: 5.7 |
Glycosylation gave an 84% yield of an inseparable 4.5:1 α:β mixture of the disaccharides, which was saponified to give the products 33α and 33β.
