Figure 1.
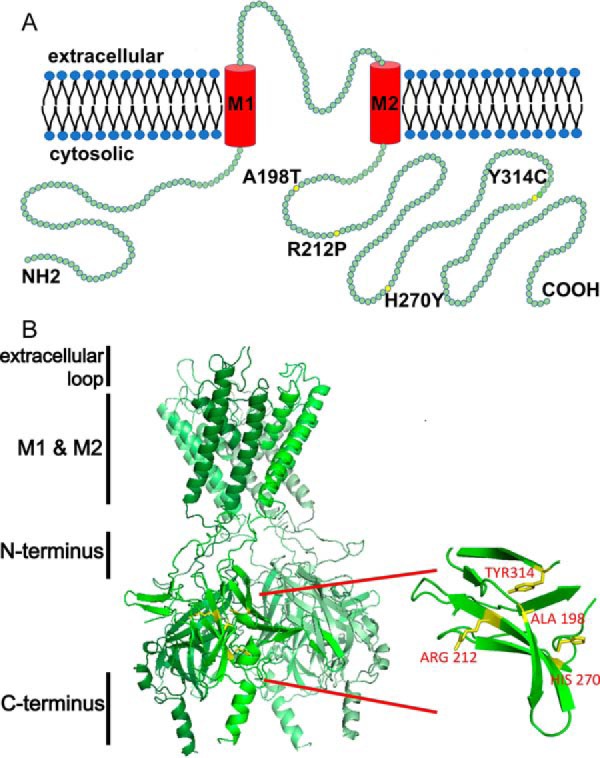
ROMK structure highlighting select mutations associated with type II Bartter syndrome. A, a linear structural model of ROMK. Each green circle represents a single amino acid. Yellow circles indicate mutations described in this study. ROMK shares a common structure with other inwardly rectifying Kir channels: two transmembrane domains (M1 and M2), a conserved potassium selectivity filter, and cytoplasmic N and C-terminal domains. Four subunits tetramerize to form the functional channel. The molecular mass of ROMK is ∼44 kDa. The cytoplasmic N and C termini represent amino acids 1–82 and 181–391, respectively. M1 represents amino acids 83–105, the extracellular loop is amino acids 106–155, and M2 represents amino acids 156–180 (70). B, four type II Bartter syndrome mutations, A198T, R212P, H270Y, and Y314C, reside in an immunoglobulin-like domain, which is assembled from β-sheets packed face-to-face, creating a core populated by highly conserved side chains. The homology model was built and images were rendered using PyMOL software. The amino acid sequence of this protein can be accessed through UniProtKB (UniProt accession number P48048-1).
