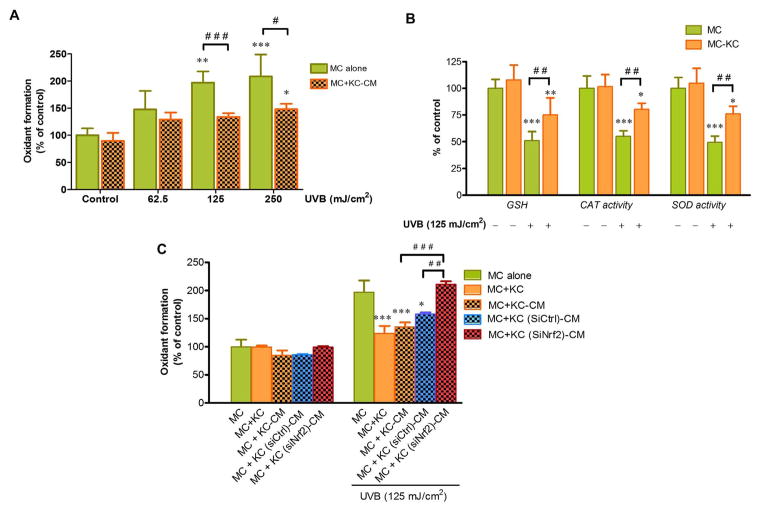
Fig. 3.
The effects of UVB-induced ROS formation and antioxidant defenses in MC co-cultured with KC: modulation by Nrf2 knockdown in KC. (A) Dose-dependent effects of UVB on oxidant formation in MC pretreated with CM from KC irradiated with UVB (62.5, 125 and 250 mJ/cm2) for 30 min. The statistical significance of differences between unirradiated MC and UVB-irradiated MC monoculture was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 versus unirradiated control MC) and between the UVB-irradiated MC monoculture and UVB-irradiated MC+KC-CM was evaluated by Student’s t-test (#P < 0.05; ###P < 0.001 versus UVB-irradiated MC monoculture). (B) GSH levels and activities of catalase and SOD were determined at 1 h after UVB (125 mJ/cm2) irradiation using a spectrofluorometer. The statistical significance of differences between unirradiated MC and UVB-irradiated cells was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 versus unirradiated control MC) and between the UVB-irradiated MC monoculture and UVB-irradiated MC+KC was evaluated by Student’s t-test (##P < 0.01 versus UVB-irradiated MC monoculture). (C) The effects of UVB (125 mJ/cm2) on oxidant formation in MC monoculture, MC co-cultured in transwell with siNrf2 or siCtrl-transfected KC and MC pretreated with the CM from siNrf2 or siCtrl-transfected KC following UVB irradiation. The statistical significance of differences was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 versus UVB-irradiated MC monoculture. ## P < 0.01; ###P < 0.001 versus UVB-irradiated MC+KC (siNrf2)-CM.