Figure 5.
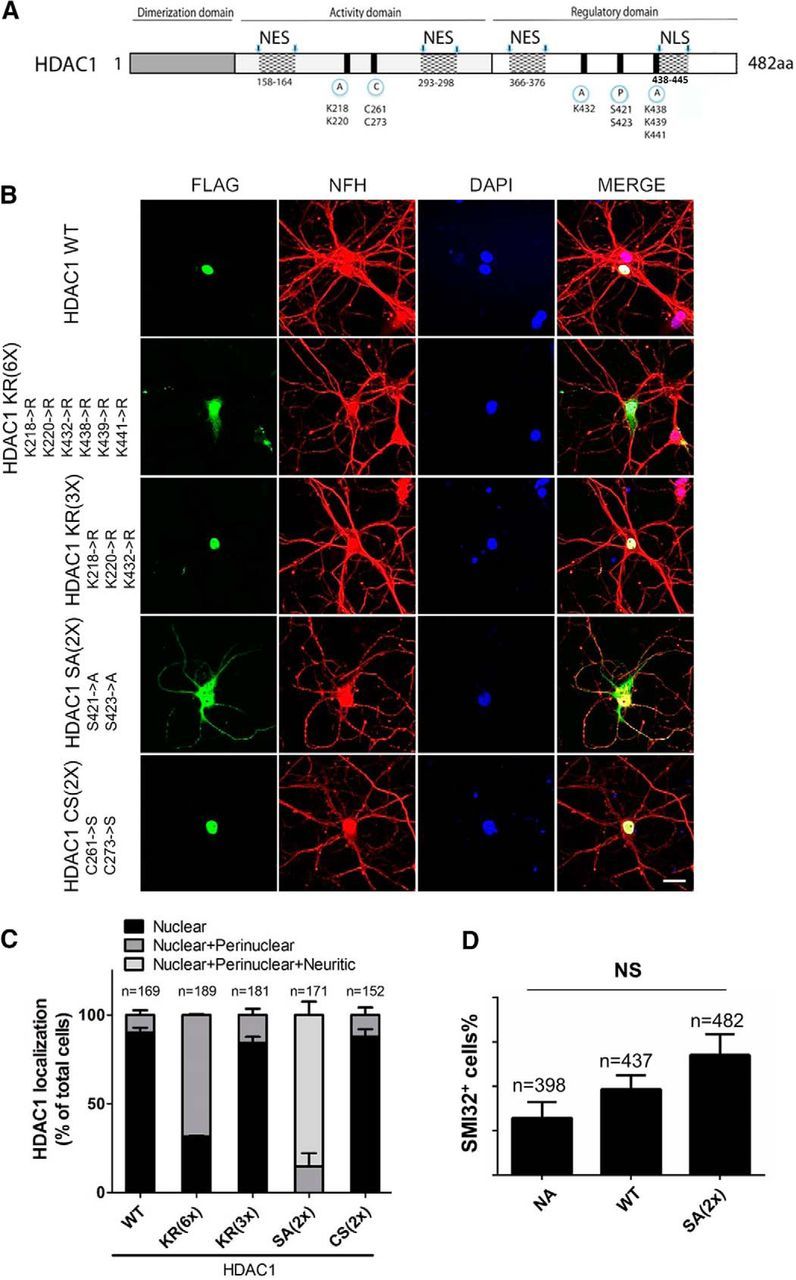
Mutation of phosphorylation sites induce HDAC1 nuclear export. A, Schematic representation of HDAC1 protein sequence displaying its domains and PTM sites. A, Acetylation; C, carbonylation; P, phosphorylation; NES, nuclear export signal. B, Primary cultures of rat hippocampal neurons transfected with FLAG-tagged HDAC1 constructs containing different mutations on PTM sites were immunostained against FLAG (green) and NFH (red) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. C, Quantification of subcellular localization of FLAG signal from B showing that only mutation of phosphorylation sites (S421, 423→A) induced localization of recombinant HDAC1 to the neuronal cytosolic processes. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. D, Quantification of neurons with SMI32+ processes over total DAPI+ cells after lentivirus-mediated overexpression of either WT or the nonphosphorylated mutant HDAC1 HDAC1 SA(2×). NA, Uninfected naive neurons. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, p > 0.05 (NS).
