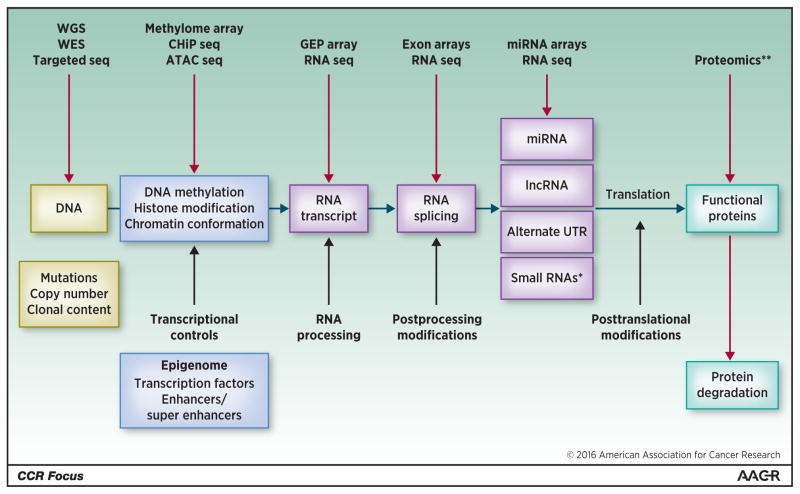
Figure 2. Next generation highthroughput and sequencing technologies provides new markers for gene profiling.
Gene expression profile results from various processes (middle row) including post-translational leading to protein modification. Several genomic analysis technologies (upper row) are available to identify various genomic abnormalities to develop an integrated approach allowing understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of multiple myeloma, risk stratification and development of personalized medicine.
Alternate UTR, alternate untranslated region; ATAC seq, Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin with high-throughput sequencing; GEP array, gene-expression profile array; lncRNA: long noncoding RNA; miRNA, microRNA; RNA seq, RNA sequencing.
*Small RNAs: small nucleolar RNA (snoRNAs), small nuclear RNA (U-RNA), small rDNA-derived RNA (srRNA).
**Protein modification such as phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, and glycosylation.
Adapted from Munshi and Avet-Loiseau (80).