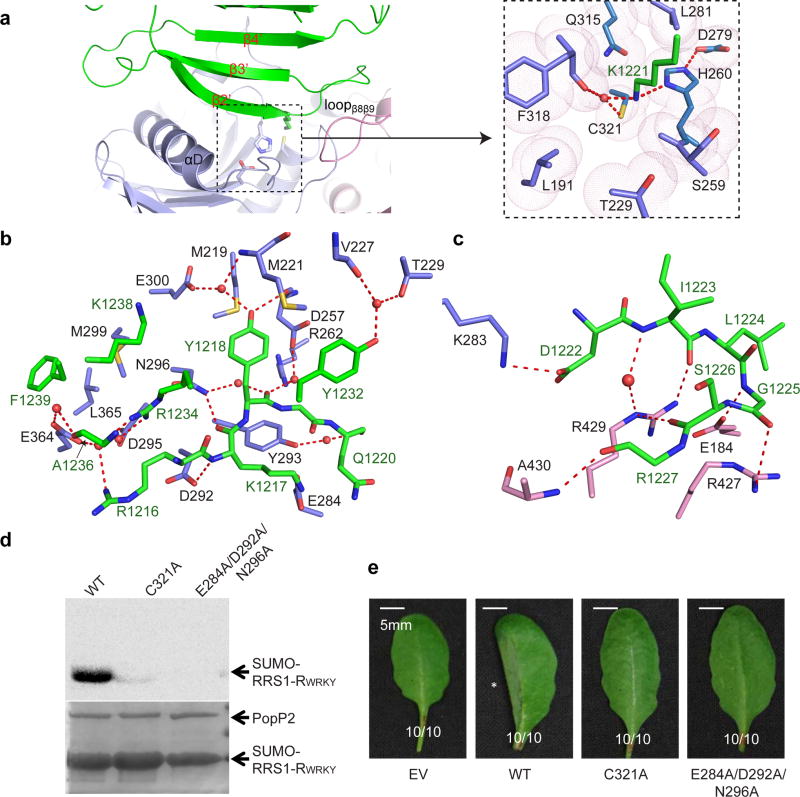
Figure 3. The PopP2 – RRS1-RWRKY interaction.
a, The interface between PopP2 and RRS1-RWRKY, with the catalytic site shown in expanded view. b, Close-up views of the interactions of PopP2 with β2, β3 and Loopβ3β4 of RRS1-RWRKY. c, Close-up views of the interactions of PopP2 with loopβ2β3 of RRS1-RWRKY. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as dashed lines, and water molecules are shown as red spheres. d, In vitro acetylation activity of wild-type (WT) or mutant PopP2. The acetylated proteins were detected by autoradiography, and the protein amount is indicated by Coomassie blue staining. e, Cell death-triggering ability of PopP2 in Arabidopsis eco. Nd-1. The asterisk indicates the cell death symptom triggered by wild-type PopP2. Ratios indicate number of leaves with indicated phenotype/total number of inoculated leaves in each treatment. Experiments in d and e were repeated twice and once, respectively, with consistent results.