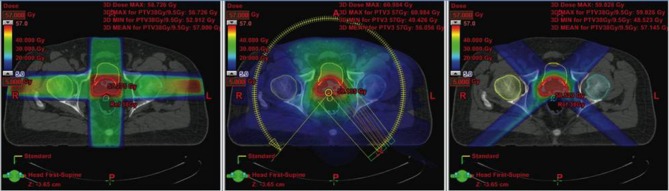
Figure 2.
Comparison of treatment plans in a patient with prostate cancer. Shown is a typical slice of the planning CT in the pelvis with different radiation plans calculated: left image: Conventional 4-field 3D-conformal plan; middle image: intensity-modulated volumetric arc plan, right image: 4-field proton plan. The arrows show the target contour (prostate, red), the rectum (black with inflated rectum balloon), and the hips. Red signifies high dose volume, green intermediate dose volume, and blue low dose volume. The rectum is the major organ that has to be spared from radiation in the case of prostate cancer. To protect the rectum, an endorectal balloon is inserted before every radiation fraction and inflated with air. The rectum balloon serves to move major parts of the rectal wall away from the prostate and the high dose volume. The volumetric arc plan spares the rectum much better and conforms the dose better to the prostate than the 3D plan. In comparison, the proton plan shows equal target coverage as the VMAT plan, but much less dose delivery to the surrounding tissue, especially the rectum and both hip bones. Copyright ©2013. Swiss Physical Society. Image and figure caption reproduced from Lang S and Riesterer O. Progress in Physics: Modern Techniques in Radiation Oncology. SPG Mitteilungen. 2013;41(36): 19–22.109