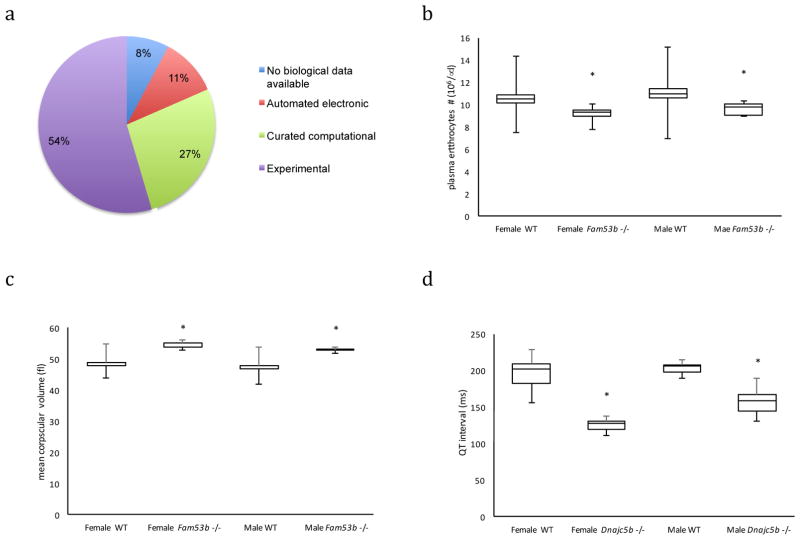
Figure 4. Novel Mouse Models of Disease –
Over 40% of IMPC strains are for genes that lack experimental evidence for function according to the Gene Ontology Consortium (A in grey). Fam53b - Fam53btm1b(EUCOMM)Hmgu homozygous mutant mice had significantly decreased red blood cell counts (B; box plot representations throughout represent first and 3rd quartiles with the line indicating the median and whiskers representing the min and max values and asterisks indicating a significant difference between mutant and same sex controls using the mixed model with a p < 0.0000. Female control=597, female homozygous=8, male control=635, male homozygous=8; linear mixed-effects model without Weight; p=2.81E-11), and enlarged erythrocytes (C; Female control=598, female homozygous=8, male control=634, male homozygous=9; linear mixed-effects model without Weight; p=0), consistent with Diamond-Blackfan Anemia (DBA, OMIM: 105560). Dnajc5b - Dnajc5btm1b(EUCOMM)Hmgu homozygous mutants displayed significantly shortened QT interval as measured by electrocardiogram (D; Female control=7, female homozygous=6, male control=7, male homozygous=8; generalized least squares without weight; p=7.41E-08), supporting a role for DNAJC5b variants associated with human variability to statin effects on cardiovascular incident frequency.