Figure 1. Nesprin1α forms filamentous structures in photoreceptors.
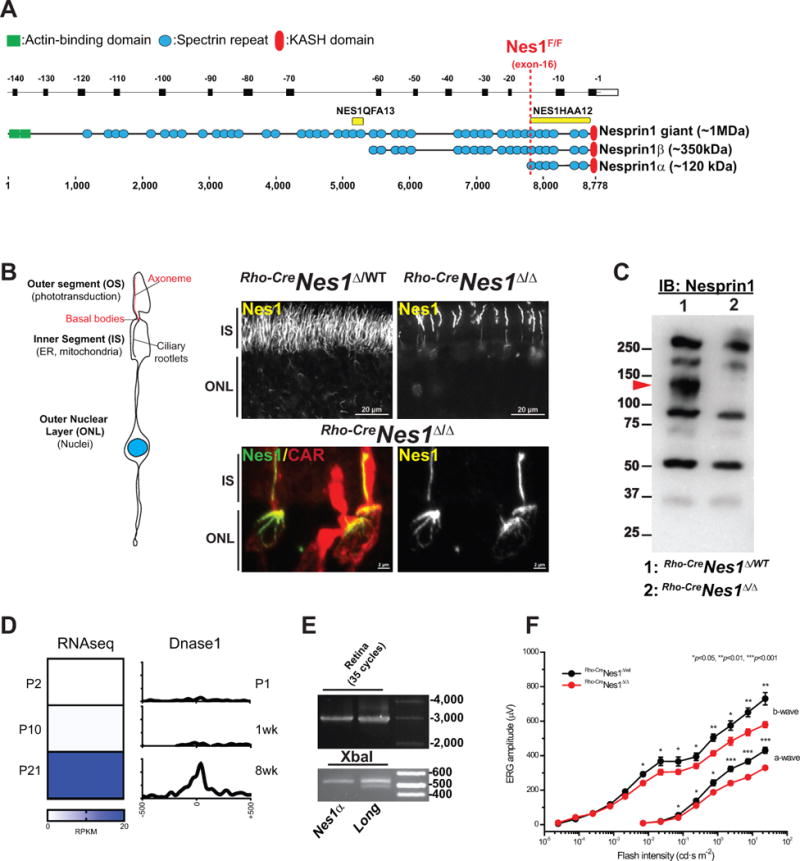
A. Alignment of Syne1 exons (top, reverse numbering) with corresponding Nesprin1 isoforms that interact with the NE through their C-terminal KASH domain. Yellow bars: epitopes used to raise NES1QFA13 and Nes1HAA12 antisera. The dashed red line denotes the position of LoxP sites flanking exon -16 in Nes1Flox/Flox mice. B. Depiction of the main compartments of photoreceptors. Nesprin1 immunolabeling of adult Rho-CreNes1Δ/WT (top left panel) and Rho-CreNes1Δ/Δ (top right panel) littermate retinas. Note the loss of Nesprin1 immunoreactivity in the IS and the ONL of Rho-CreNes1Δ/Δ rods. Lower panels: Maximum intensity projection of Nesprin1 localization in cones within Rho-CreNes1Δ/Δ retinas emphasizing similar Nesprin1 filaments lining the IS and “aster-like” structures capping the apical side of cone nuclei. CAR: Cone arrestin used to label cones. IS: inner segments; ONL: outer nuclear layer. See also Figure S1A and S1B. C. Nesprin1 immunobloting of adult Rho-CreNes1Δ/WT and Rho-CreNes1Δ/Δ retina lysates showing the loss of a ~120 kDa immunoreactive band in Rho-CreNes1Δ/Δ retinas (arrowhead). See also Figure S1C and S1D. D. Left: Relative abundance (in reads per kilobase per million mapped reads, RPKM) of reads encompassing exon-16b, which is specifically included in Nesprin1α transcripts, at different postnatal (P) stages of retinal development. Right: DNase I hypersensitivity (reads per base per million) at similar developmental stages showing the corresponding activation of the Nesprin1α promoter. E: Upper panel: RT-PCR amplification (35 cycles) of Nesprin1α (Nes1α) or of transcripts encoding larger isoforms of Nesprin1 (Long) performed on total RNA from retina (see also Figure S1E, F for more details). Lower panel: XbaI digests emphasizing the absence of the 476 bp restriction fragments (asterisk) indicative of exon-2 alternative splicing in retinal Nesprin1α transcripts. See also Figure S1E and S1F. F. Scotopic electroretinograms of 2.5 month-old Rho-CreNes1Δ/Δ (red traces; n=4) and Rho-CreNes1Δ/WT (black traces; n=4) mice. Note a ~20% decrease of ERG a- and b-waves amplitudes in Rho-CreNes1Δ/Δ mice compared to controls.
