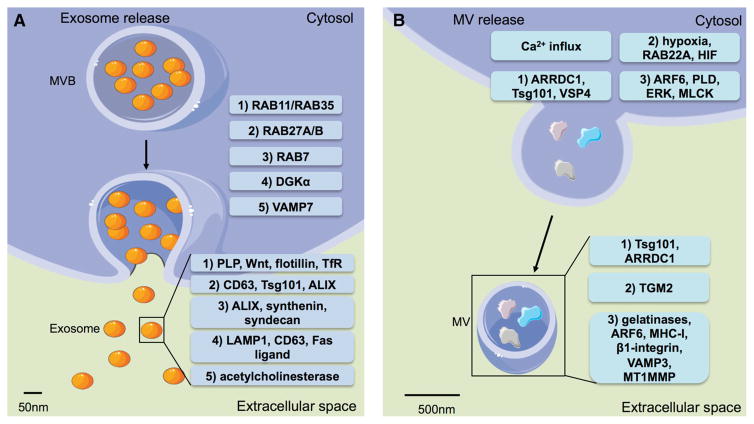
Fig. 2.
Molecular machineries of EV release. a Proteins involved in controlling the fusion of MVBs with the outer membrane to the plasma membrane, resulting in release of exosomes. Five different machineries have been described so far; 1 RAB11 and RAB35 facilitate the fusion of MVBs to the plasma membrane, releasing exosomes containing PLP, Wnt, flotillin, and TfR; 2 RAB27A and RAB27B promote release of exosomes loaded with CD63, TSG101, and ALIX; 3 RAB7-dependent release yields release of exosomes harboring ALIX, synthenin, and syndecan; 4 DGKαprotein is implicated in release of exosomes carrying LAMP1, CD63, and Fas ligand; and 5 VAMP7 regulates the membrane fusion associated with release of acetylcholinesterase-containing exosomes release. b EV released via the outward budding and fission of the plasma membrane controlled by different proteins and extracellular signaling results in release of MVs with a distinct protein profile. Three pathways have been described including markers found in released MVs: a ARRDC1, TSG101, and VSP4 are responsible for the shedding of MVs containing TSG101 and ARRDC1; b hypoxia following expression of RAB22A via HIF, characterizes the secretion of EVs carrying TGM2; and c the ARF6, PLD, ERK, and MLCK cascade induces release of EVs containing gelatinases, ARF6, MHC-I, β1-integrin, VAMP3, and MT1MMP. [Components in image derived from Servier Medical Art Powerpoint image bank (Servier 2016)]