Figure 6. IL-17 reduces cyclin D1 expression by activating CMA.
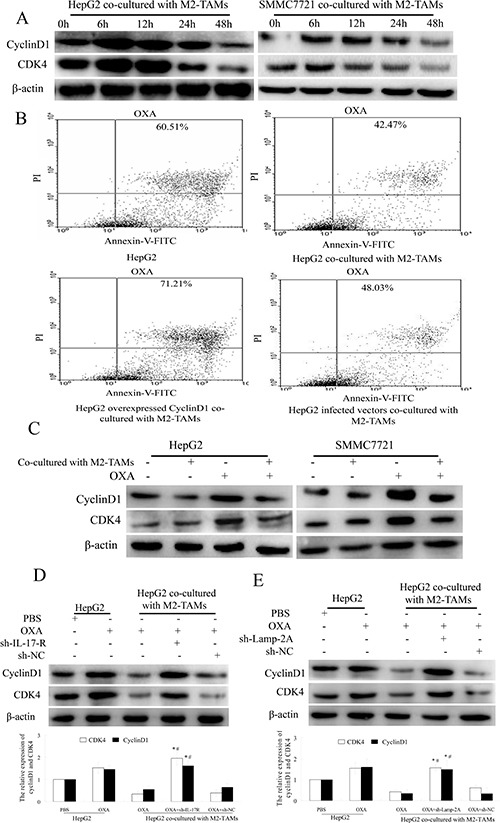
(A) HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells were co-cultured with M2-TAMs for 24 h and then treated with 20 μg/mL oxaliplatin for various times. Cyclin D1 and CDK4 were detected by Western blotting. (B) HepG2 cells were transfected with a cyclin D1 overexpression plasmid or a negative control vector and then co-cultured with M2-TAMs for 24 h. After oxaliplatin (20 μg/mL) treatment for another 24 h, apoptotic cells were detected by flow cytometry. (C) HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells were cultured with or without M2-TAMs for 24 h and then treated with 20 μg/mL oxaliplatin for another 24 h. Cyclin D1 and CDK4 were detected by Western blotting. (D) sh-IL-17R HepG2 cells were cultured with or without M2-TAMs for 24 h and then treated with 20 μg/mL oxaliplatin for another 24 h. Cyclin D1 and CDK4 were detected by Western blotting. (E) sh-LAMP-2A HepG2 cells were cultured with or without M2-TAMs for 24 h and then treated with 20 μg/mL oxaliplatin for another 24 h. Cyclin D1 and CDK4 were detected by Western blotting.
