Figure 5. Specificity of the cytotoxic effect of 2h9-vc-MMAE, and importance of cathepsin-mediated linker cleavage.
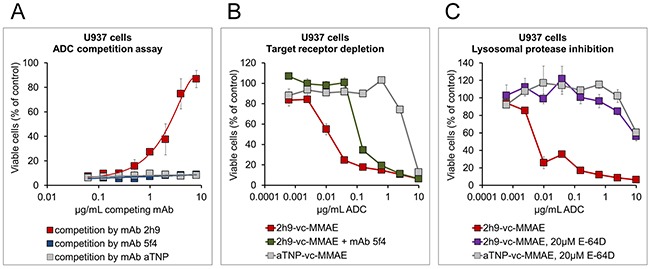
MTS-based cell viability assays were performed as in Figure 4, except that additional reagents were added as indicated. (A), receptor competition assay with unmodified mAbs. Viability curves obtained upon incubation of U937 cells with 1 μg/mL of 2h9-vc-MMAE in the simultaneous presence of increasing amounts of potential competitor mAbs, using either mAb 2h9 (red), mAb aTNP (grey) or a different uPARAP-directed mAb (5f4; blue). Only mAb 2h9 rescues the cells from 2h9-vc-MMAE mediated toxicity. (B), effect of target receptor depletion on ADC toxicity. Viability curves of U937 cells obtained with a concentration series of 2h9-vc-MMAE, either without pretreatment of cells (red), following a 3 hour preincubation with uPARAP-depleting mAb 5f4 (green; see text), or obtained with a concentration series of ADC aTNP-vc-MMAE (grey). Preincubation with mAb 5f4 decreases the impact of 2h9-vc-MMAE on cell viability approximately 10-fold. (C), inhibition of lysosomal ADC linker cleavage and drug release. Viability curves of U937 cells obtained in the presence of ADCs 2h9-vc-MMAE (red), aTNP-vc-MMAE (grey), or 2h9-vc-MMAE following preincubation of cells with 20 μM of an inhibitor of lysosomal proteases (E-64D, purple). Incubation in the presence of E-64D abrogates the toxic effect of 2h9-vc-MMAE.
