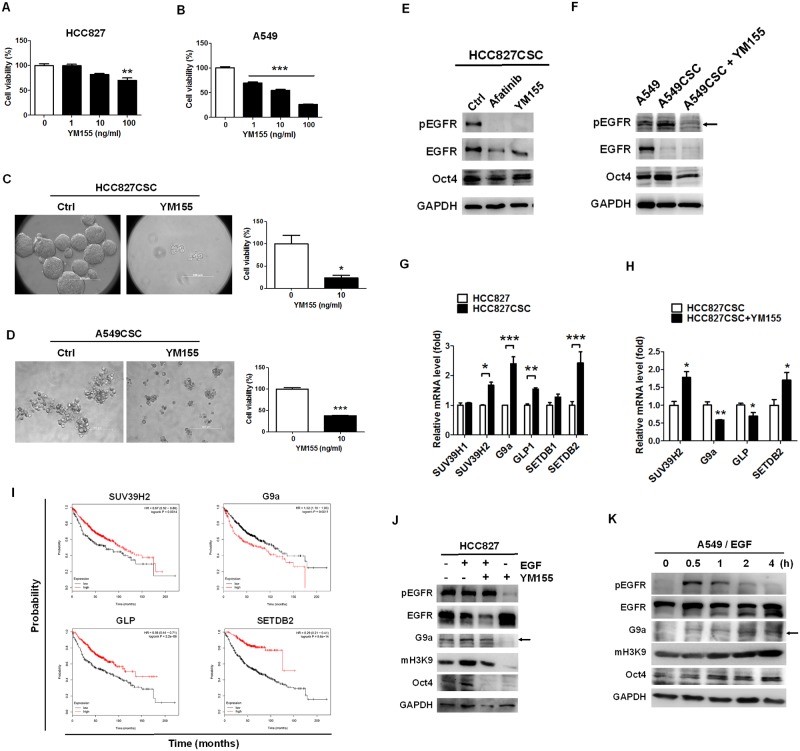
Fig 2. YM155 significantly reduced tumorsphere formation and inhibited EGFR autophosphorylation and G9a expression.
YM155 is reported to suppress cancer stemness; therefore, we used this compound to investigate the cellular mechanism of tumorsphere formation. To compare the cytotoxic capacity of YM155 against tumorsphere formation and parental cell lines, YM155 was applied to HCC827 and A549 cells in the stemness cultured or integrated medium. (A) YM155 significantly reduced HCC827 cells when used at a dose of 100 ng/mL (**p < 0.01) and (B) A549 cells when used at a dose of 1 ng/mL (***p < 0.001). (C) Microscopy revealed that 10 ng/mL of YM155 considerably inhibited the formation of HCC827 and (D) A549CSC tumorspheres and resulted in a lower cell viability. (E) Because EGFR overexpresses in HCC827 and A549 cells, and because YM155 has been reported to suppress EGFR, we investigated the autophosphorylation status of EGFR in HCC827- and A549-derived tumorspheres. EGFR phosphorylation was blocked by YM155 in HCC827-derived tumorspheres, whereas afatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, was used as a control. (F) Moreover, YM155 inhibited EGFR autophosphorylation in A549-derived tumorspheres and reduced Oct4 expression. (G) The methylation on H3K9 was high in HCC827-derived tumorspheres; therefore, we investigated the mRNA levels of the SET domain-containing proteins, particularly those functioning in H3K9 methylation, in HCC827 CSCs compared with parental HCC827 cells. The results revealed that the mRNA of SUV39H2, G9a, GLP, and SETDB2 increased in HCC827 CSCs. (H) In addition, YM155 significantly reduced the mRNA levels of G9a and GLP but increased those of SUV39H2 and SETDB2. (I) To confirm the significant roles of tumorsphere-expressed SUV39H2, G9a, GLP, and SETDB2 in lung adenocarcinoma, the Kaplan–Meier method was used for investigating the relationship between the mRNA levels of SUV39H2, G9a, GLP, and SETDB2 and the survival rate in 2,437 patients with lung cancer; the mean follow-up period was 49 months. The results revealed that an elevated mRNA level of G9a was associated with a lower overall survival rate in the patients with lung adenocarcinoma, but the remaining three genes yielded controversial results. Higher gene expression levels are indicated in red. (J) We investigated whether EGFR could downregulate G9a expression in HCC827 cells. We found that YM155 reduced EGF-induced G9a expression, H3K9 methylation, and Oct4 expression in HCC827 cells. HCC827 cells were treated with 20 ng/mL of EGF with or without 10 ng/mL of YM155. (K) HCC827, an EGFR-mutant strain, can induce autophosphorylation; therefore, we investigated and validated EGFR-regulated G9a expression in EGFR wild-type A549 cells. A549 cells treated with 20 ng/mL of EGF expressed immediate EGFR autophosphorylation in 0.5 h and subsequent G9a, mH3K9, and Oct4 expression. The results indicated that EGF induced the expression of G9a and Oct4 in lung cancer. Scale bar: 100 μm. *p < 0.05.