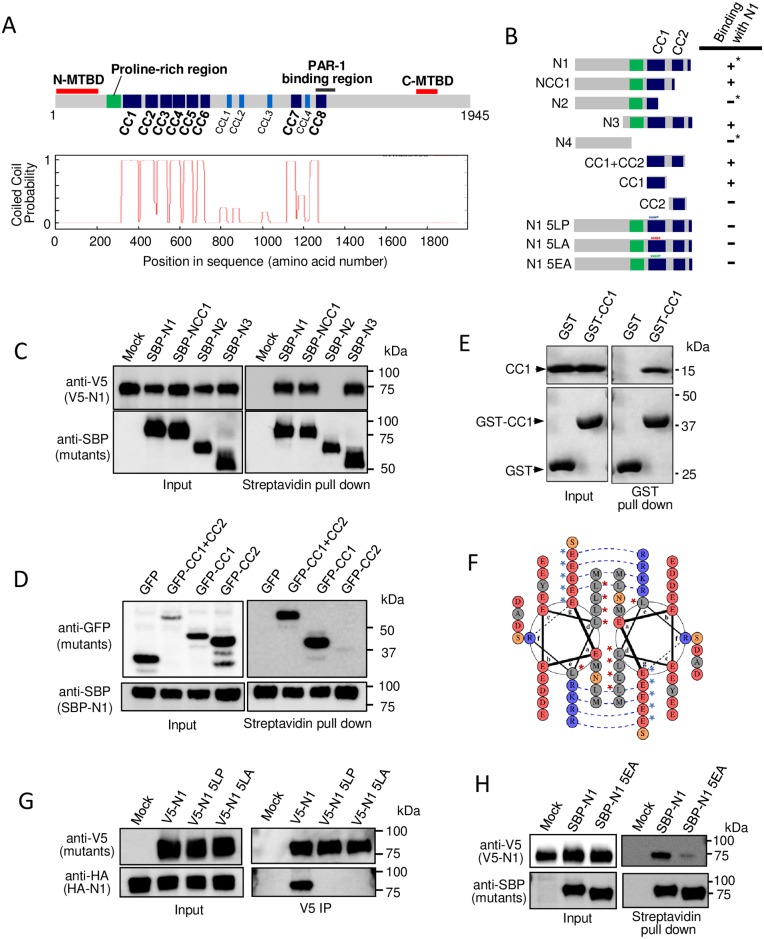
Fig 1. The first coiled-coil motif is critical for oligomerization of the N-MTBD of MTCL1.
(A) Domain organization of mouse MTCL1 (top) and the coiled-coil probability of each motif predicted by Coils (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/COILS_form.html) (bottom). (B) Schematic representation of the N-terminal mutants used in the following experiments and the summary of results. Asterisks indicate previously reported results [21]. (C) Streptavidin pull-down assays performed with extracts of HEK293T cells co-expressing SBP-tagged MTCL1 mutants and V5-tagged N1. (D) Streptavidin pull-down assays performed with extracts of HEK293T cells co-expressing SBP-tagged N1 and GFP-tagged mutants. (E) GST pull-down assays performed with a mixture of the purified CC1 fragment and GST or GST-CC1. (F) Helical wheel presentation of the amino acid sequence of the first half of CC1. Blue dotted lines indicate predicted salt bridges enhancing the CC1-CC1 homo-interaction. Red asterisks indicate leucine residues mutated in 5LP and 5LA mutants. Blue asterisks indicate glutamate residues mutated in the 5EA mutant. (G) Immunoprecipitation assays performed using an anti-V5 antibody and extracts of HEK293T cells co-expressing V5-tagged mutants and HA-tagged N1. (H) Streptavidin pull-down assays performed with extracts of HEK293T cells co-expressing V5-tagged N1 and SBP-tagged mutants.