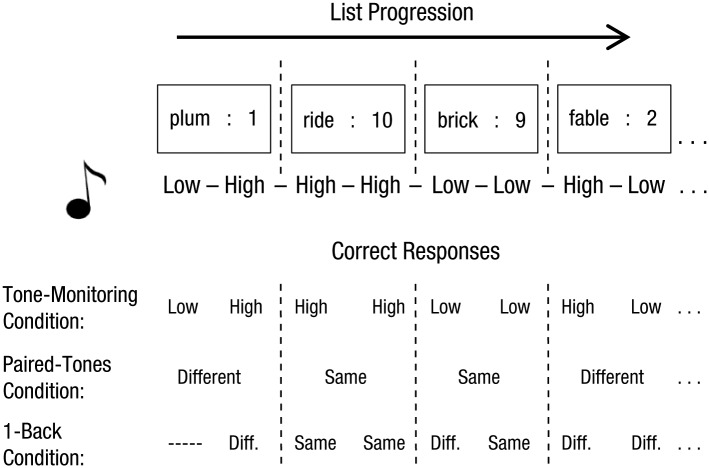
Fig. 3.
Illustration of the design of Experiment 2. As participants saw each to-be-remembered word (along with its point value), they heard two consecutive tones (top rows). Each tone was pseudorandomly chosen to be low or high pitched. In the three experimental conditions (bottom rows), participants had to identify each tone as low or high (tone-monitoring condition), identify the two tones as the same or a different pitch (paired-tones condition), or identify whether each tone was the same as or different from the previous tone (1-back condition). In a fourth condition (the full-attention condition), participants completed the primary task, but no tones were played.