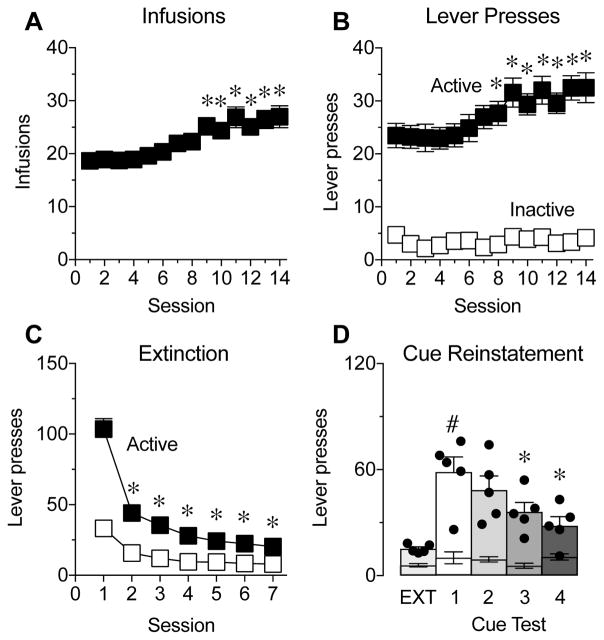
Figure 1. Intermittent access to cocaine self-administration leads to escalation of cocaine intake.
(A,B) Number of infusions earned (A) and active (black squares) and inactive (white squares) lever presses (B) during 14 sessions of intermittent access to cocaine self-administration (N=38; data is pooled from all of the DREADD cocaine self-administration experiments). *P<0.05 compared to session 1, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (C) Number of active (black squares) and inactive (white squares) lever presses during the first 7 days of extinction (EXT). *P<0.05 compared to session 1, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Active (bars and dots) and inactive (lower error bars) lever presses during extinction (Data averaged across extinction sessions before and between the cue tests) and 4 cue-induced reinstatement tests (N=5). #P<0.05 compared to EXT, Sidak multiple comparisons test; *P<0.05 compared to cue test 1, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data represent mean ± SEM.