Figure 6.
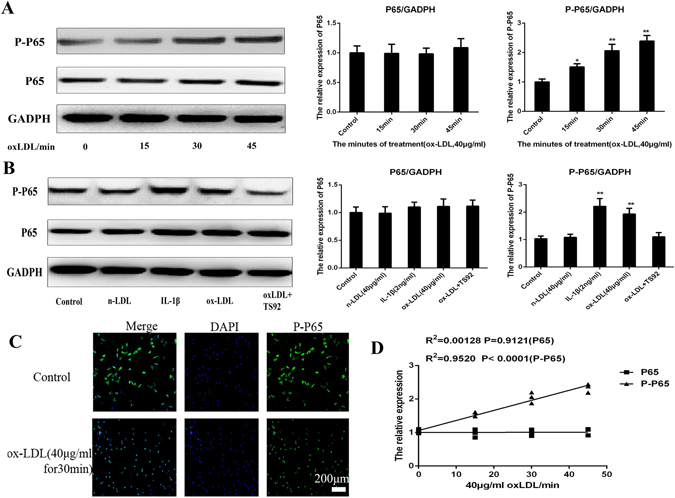
OxLDL can increase the expression of MMP3 by activating the NF-κB signal pathway. (A) Western blotting analysis for the protein expressions of P65 and PP65. Nucleus pulposus cells were treated with 40 μg/ml oxLDL for different periods (0, 15, 30, 45 min). The expressions of P65 and PP65 was quantified. Data were presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (B) Western blotting analysis for the protein expressions of P65 and PP65. NPC were respectively incubated with 40 μg/ml n-LDL, 2 ng/ml IL-1β, 10 μM ascorbic acid, 40 mg/ml ox-LDL, or preincubated with 15 mg/ml anti-human LOX-1 mAb (TS92) for 24 h than stimulated with ox-LDL for 48 h. The cells without oxLDL treatment were served as control. It shows that IL-1β and ox-LDL could improve the expression of PP65 (P < 0.01); n-LDL did not affect PP65 expression (P > 0.05) and pretreatment of NPCs with TS92 significantly suppressed the increase in expression of PP65 by ox-LDL. A one-way ANOVA were used for statistical assessments. (C) Representative fluorescent microscopic images of Hoechst/PI double stained nucleus pulposus cells showing that the 40 μg/ml oxLDL can promote the PP65 enter into the cell nuclear from cytoplasm from 0–45 min (only show 30 min). Bars = 200 μm. (D) The Correlations analysis between the stimulate period and the expression of P65, PP65 were performed (R2PP65 = 0.00128, P < 0.9121; R2P65 = 0.952, P < 0.0001). Data are presented as means ± SD. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).
