Figure 1.
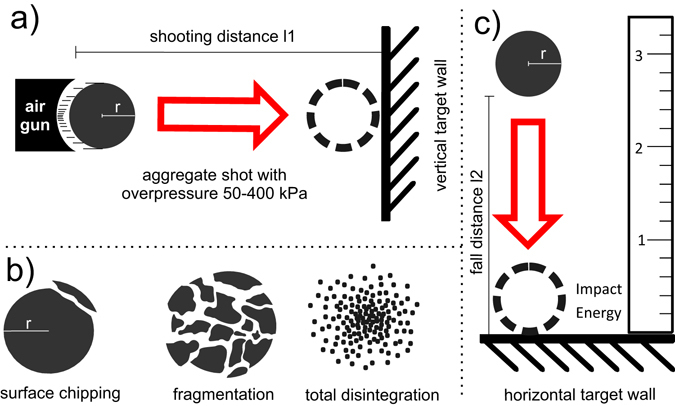
(a) Pressurized air-gun setup at Aarhus University, Denmark. Aggregates were shot with overpressure against a vertical metal wall. Applied overpressures ranged between 0.5 and 4 bar, resulting in impact velocities of 2.9–7.8 m.s−1. (b) Impact setup at LMU Munich, Germany. Aggregates were dropped from heights between 5 and 200 cm onto a metal plate. Impact speed was monitored with a high-speed camera and used to calculate impact energy. (c) Modes of break-up that were observed throughout experiments: surface chipping (<10 wt% loss of material from parent aggregate), fragmentation (10–90 wt% material loss from parent aggregate) and total disintegration (>90 wt% material loss from parent aggregate).
