Figure 4.
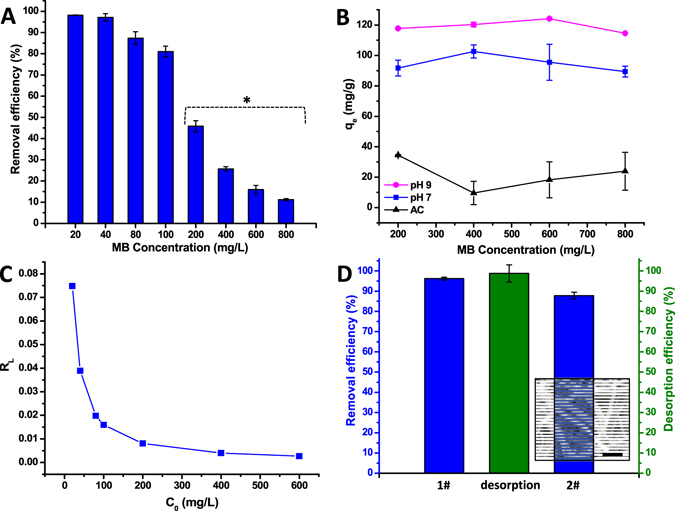
Removal efficiency, adsorption capacity of poly-CD nanofibrous membrane and comparison with activated carbon (AC) and reusability of poly-CD membrane. (A) MB removal efficiency (%) of poly-CD membrane against concentration. The adsorbed amount of MB decreases gradually by the increasing dye concentration (n = 3). (B) Comparative adsorption capacity (qe (mg/g)) graphs of poly-CD membrane (for pH = 7 and pH = 9 MB solutions) and AC are plotted for four different MB concentrations (*200–800 mg/L). Poly-CD membrane (pH = 7) indicate significantly higher capacity compared to AC. The adsorbed MB amount can be drawn up easily by adjusting the pH = 9 (n = 3). (C) RL graphs for the adsorption of MB indicating the high tendency between MB and adsorbent, and favorable uptake process. (D) The reusability of poly-CD membrane. The desorption of MB from poly-CD membrane is achieved by washing with methanol solution containing 5% (v/v) HCl. The practical recovery is provided and poly-CD membrane offers almost the same adsorption potential for the second cycle. The inset SEM image of poly-CD membrane after reusability tests (scale bar-10μm) confirms that the fiber morphology of poly-CD membrane is still preserved after the adsorption tests (n = 3).
