Fig. 3.
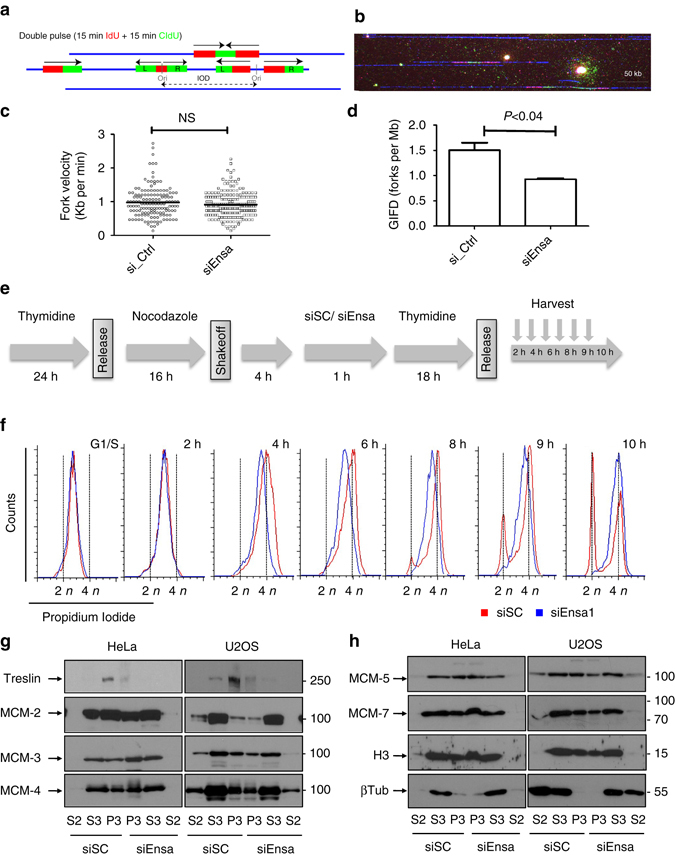
Ensa KD increases S-phase length by decreasing fork number without affecting origin licensing. a Diagram depicting IdU (red)–CldU (green) double pulse analysis by DNA combing. b Representative image of a triple-stained DNA fibre: IdU (red)–CldU (green)–DNA (blue). c Fork velocity (Kb/min) and d global instant fork density (GIFD) values (fork per Mb) are represented. Mean ± standard deviation and p-value obtained by using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-tests, are represented. Data pooled from four biological replicates. e Diagram representing the experiment in which HeLa cells were blocked in G1–S phase by thymidine for 24 h and subsequently released with fresh medium containing nocodazole (50 ng/ml) for a supplementary period of 16 h before shakeoff. Four hours later, released cells were transfected with siSC or siEnsa, and after 1 h, supplemented with fresh medium containing thymidine for an additional 18 h incubation. Cells were then released and recovered at the indicated times for FACS analysis. f FACS profiles of SC (red) and Ensa (blue) siRNA-treated cells at different time points after release are shown. g HeLa and U2OS cells were transfected with scramble (siSC) or Ensa (siEnsa) siRNAs and 48 h later processed for chromatin isolation as reported in Methods section. Cytosolic (S2) and nuclear (S3) soluble fractions as well as chromatin fraction (P3) were then used for western blot analysis to determine Treslin and MCM 2, 3 and 4 levels. h As for g, except that MCM 5 and 7, histone H3 and β-tubulin levels were checked. IOD, inter-origin distances; Ori, replication origin
