Figure 4.
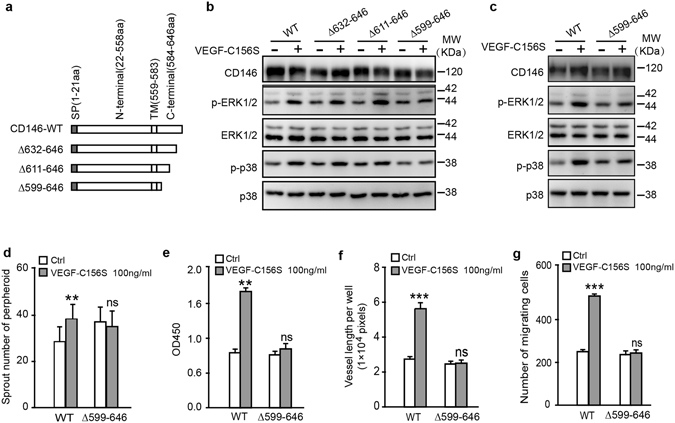
Functional cytoplasmic domain of CD146 in VEGF-C induced cell activation. (a) Diagrammatic representation of C-terminal truncations of CD146 at the intracellular domain. (b) Phosphorylation and expression of ERK1/2 and p38, elicited from VEGF-C156S, were analyzed by WB. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding truncated versions of CD146 as shown in (a). (c–g) HDLECs transfected with plasmids encoding CD146-WT and CD146-∆599-646 were subjected to signaling activation assay (c), spheroid sprouting assay (d), proliferation assay (e), tube formation assay (f) and transwell migration assay (g). VEGF-C was applied at the indicated concentration. Data were expressed as means ± SEM from 3 independent experiments (n = 12 in each group of c–g,). Significant difference was determined by Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, no significant difference). Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S4.
