Figure 5.
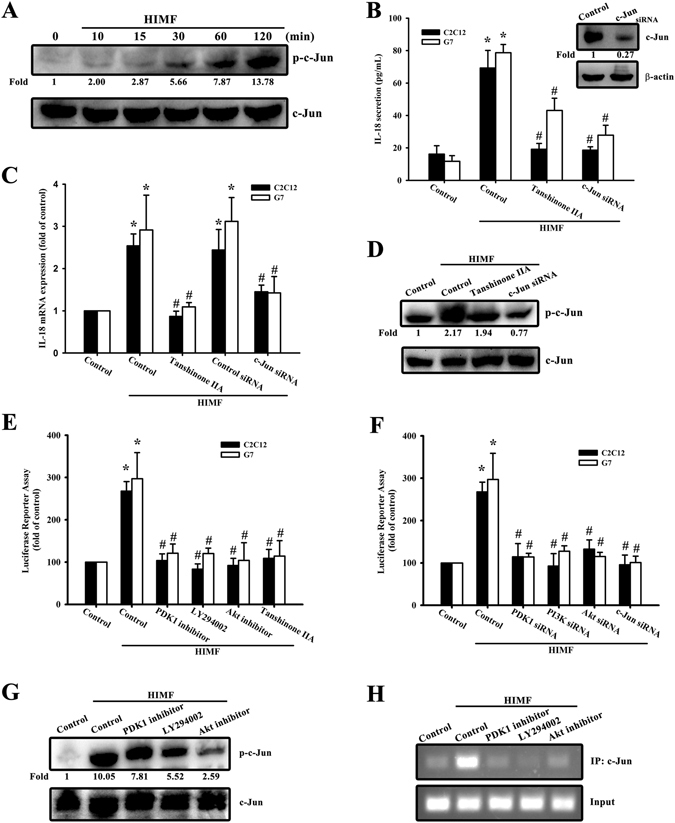
HIMF induces IL-18 production through AP-1. (A) Cells were incubated with HIMF (3 nM) for indicated time intervals and cell lysates were immunoblotted with an antibody specific for phospho-c-Jun. (B) Cells were transfected with siRNA against c-Jun for 24 h, and c-Jun protein expression was analyzed (upper panel). Cells were treated for 30 min with Tanshinone IIA or transfected with a c-Jun siRNA for 24 h, then stimulated with HIMF for 24 h, and the conditioned media was collected and examined by ELISA (lower panel). (C) HIMF-induced IL-18 mRNA was inhibited by Tanshinone IIA or a c-Jun siRNA. (D) HIMF-induced c-Jun phosphorylation was inhibited by a Tanshinone IIA or c-Jun siRNA. (E) Cells were treated with the PDK1 inhibitor, LY294002, an Akt inhibitor, or Tanshinone IIA for 30 min, then incubated with HIMF for 24 h. AP-1-luciferase activity was measured, and the results were normalized to β-galactosidase activity. (F) Cells were co-transfected with either AP-1-luciferase plasmid or siRNA against PDK1, PI3K, Akt, or c-Jun for 24 h, then stimulated with HIMF. AP-1-luciferase activity was measured, and the results were normalized to β-galactosidase activity. (G) Cells were treated with the PDK1 inhibitor, LY294002, or an Akt inhibitor for 30 min, then stimulated with HIMF for 120 min, and phospho-c-Jun protein expression was analyzed. (H) The recruitment of c-Jun to the IL-18 promoter was analyzed using the ChIP assay. Results are expressed as the means ± SEM of four independent experiments. *p < 0.05 as compared with the control group. # p < 0.05 as compared with HIMF-treated group.
