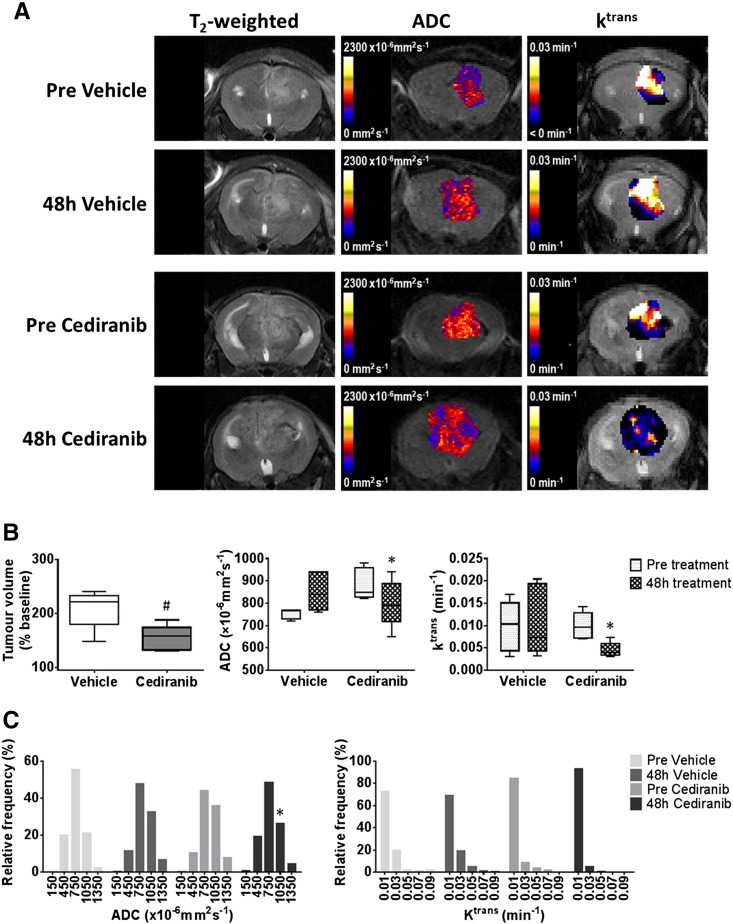
Figure 3.
Anatomical, diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of intracranial MDA-MB-231 LM2–4 tumors treated with cediranib.
(A) T2-weighted MRI images, and associated parametric ADC and Ktrans maps, from representative intracranial MDA-MB-231 LM2–4 tumors prior to, and following, 48 hours treatment with either vehicle or 6 mg/kg cediranib daily, as indicated. (B) Quantification of the change in tumor volume over the 48 h treatment period, and of ADC and Ktrans prior to, and following, treatment with either vehicle (n = 5) or cediranib (n = 6). (C) Frequency distributions of all tumor ADC and Ktrans voxels. Distributions were divided into 5 equally sized bins for each dataset, using 0–300, 300–600, 600–900, 900–1200, 1200–1500×10−6mm2sec−1 for ADC and 0–02, 0.2–0.4, 0.4–0.6, 0.6–0.8, 0.8–0.1 min−1 for Ktrans. #P < .05, unpaired Student's t test between vehicle and cediranib-treated cohorts. *P < .05, paired Student's t test.