Fig. 5.
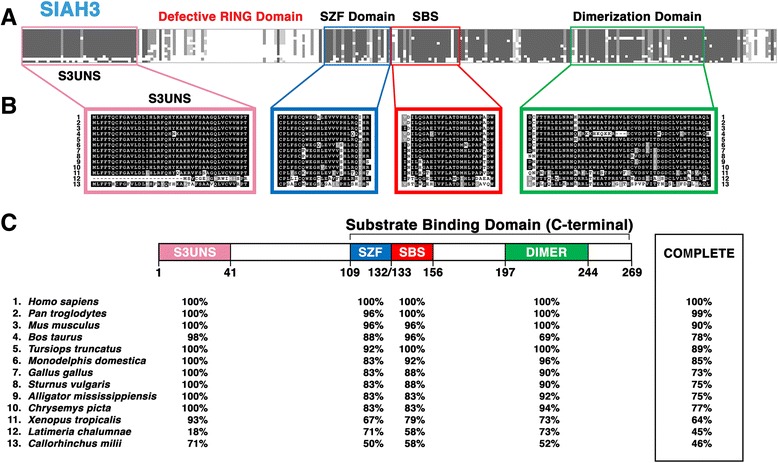
Sequence alignment of the vertebrate SIAH3 subfamily reveals its invariant amino acid residues, absence of RING domain, and conserved structural motifs. Sequence comparison of SIAH3 proteins from 13 representative vertebrate species (#1-#13) is shown. a The level of amino acid conservation in the N-terminal fragments is high, while the portion of the protein sequences that would be expected to contain the RING domain is highly divergent compared to SIAH1 and SIAH2. Four key functional domains are marked in four distinct colors: SIAH3 unique N-terminal sequence (S3UNS, pink), SZF domain (blue), SBS (red) and DIMER domain (green). b Schematic illustration of amino acid conservation within the 4 distinct domains of the SIAH3 sequences is shown. Amino acid identity is shown as white letters in a black box, amino acid similarity is shown as white letters in a grey box, and amino acid divergence is shown as black letters in a white box . c The percentages of amino acid conservation in each distinct domain and the entire SIAH3 sequence between human and each of the representative vertebrate species are shown. The diagram of the domain architecture was based on Homo sapiens SIAH3
