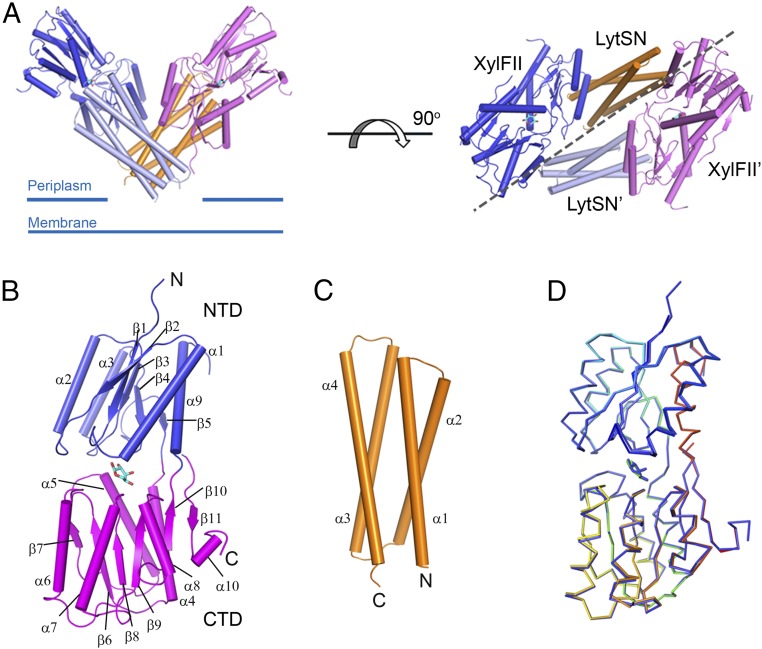
Fig. 1.
Structure of the XylFII-LytSN-xyl complex. (A) Structure of the WT XylFII-LytSN complex with bound d-xylose (XylFII-LytSN-xyl). (Left) Side view of the XylFII-LytSN heterotetramer. (Right) Top view of the XylFII-LytSN heterotetramer. XylFII, XylFII′, LytSN, and LytSN′ are shown in blue, magenta, orange, and gray, respectively. d-xylose molecules are shown as cyan sticks. (B) Structure of WT XylFII with bound d-xylose. The NTD and CTD are shown in blue and magenta, respectively. (C) Structure of WT LytSN. (D) Superimposed structures of XylFII-xyl and XylFII in the XylFII-LytSN-xyl complex. XylFII-xyl and XylFII in the XylFII-LytSN-xyl complex are shown in rainbow and blue, respectively.