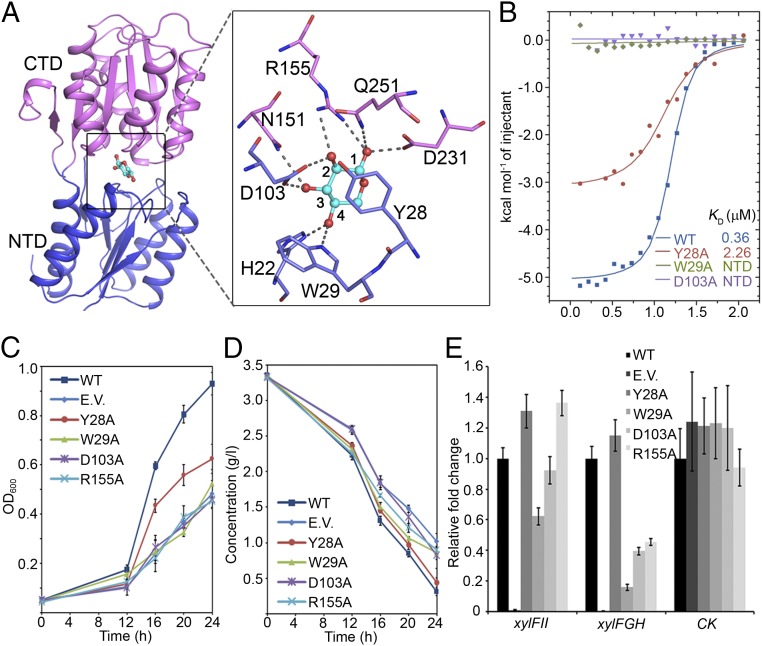
Fig. 2.
The d-xylose binding site of XylFII. (A) Interaction of amino acid residues with d-xylose in the binding site. The bound d-xylose (cyan) is depicted as a ball-and-stick model. The side chains of the residues involved in the specific binding of d-xylose are shown in a zoom-in view. (B) Binding affinities of d-xylose to XylFII-LytSN and mutants measured using ITC. Binding curves of XylFII-LytSN (WT) and mutants XylFIIY28A-LytSN (Y28A), XylFIIW29A-LytSN (W29A), and XylFIID103A-LytSN (D103A) measured by ITC are shown in blue, red, green, and purple, respectively. (C) Growth of C. beijerinckii affected by the d-xylose binding site mutations. The growth rates were monitored by transforming XylFII (WT), empty pXY1 vector (EV), XylFIIY28A (Y28A), XylFIIW29A (W29A), XylFIID103A (D103A), or XylFIIR155A (R155A) genes to the xylFII mutant strain and growing them in YP2 medium with d-xylose as the sole carbon source. The bars indicate the SDs of three independent experiments. (D) d-xylose consumption of curve of C. beijerinckii affected by the d-xylose binding site mutations. The residual d-xylose in the medium were monitored by transforming XylFII (WT), empty pXY1 vector (EV), XylFIIY28A (Y28A), XylFIIW29A (W29A), XylFIID103A (D103A), or XylFIIR155A (R155A) genes to the xylFII mutant strain and growing them in YP2 medium with d-xylose as the sole carbon source. The bars indicate the SDs of three independent experiments. (E) Expression levels of genes affected by the d-xylose binding site mutations. The expression of xylFII, the downstream target d-xylose ABC transporter xylFGH genes, and a gene encoding pullulanase (control; CK) were measured by qRT-PCR. Gene expression levels are represented as fold differences normalized to WT. The error bars indicate the SDs of three independent experiments.