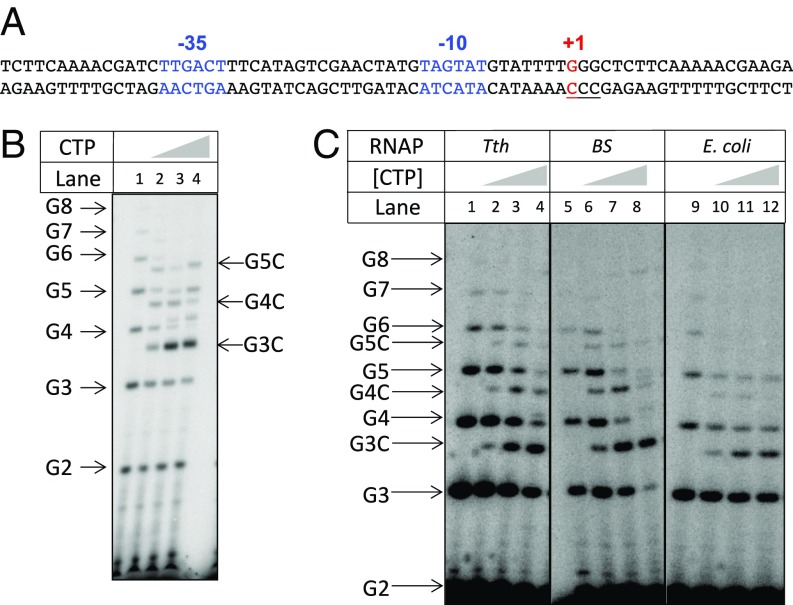
Fig. 1.
Characterization of reiterative transcription by the T. thermophilus RNAP. (A) DNA sequence of the B. subtilis pyrG promoter region. The −35 and −10 regions (blue) and the +1 transcription start site (red) are indicated. The template strand CCC track (from +1 to +3) that permits reiterative transcription is underlined. (B) In vitro reiterative transcription by the T. thermophilus RNAP using a double-stranded DNA containing the pyrG promoter shown in A as template. Transcription assays were performed in the presence of GTP (100 μM GTP plus 1 μCi [γ-32P]GTP) and different concentrations of CTP (0, 1, 10, and 100 μM). The positions of the reiterative poly-G and the poly-G + C products are indicated. Note that poly-G transcripts migrate slower than same-length poly-G + C transcripts. (C) In vitro reiterative transcription with the synthetic scaffold shown in Fig. 2A and different RNAPs. Transcription assays were performed as in B. RNAPs used for these reactions are indicated (Tth, T. thermophilus; BS, B. subtilis).