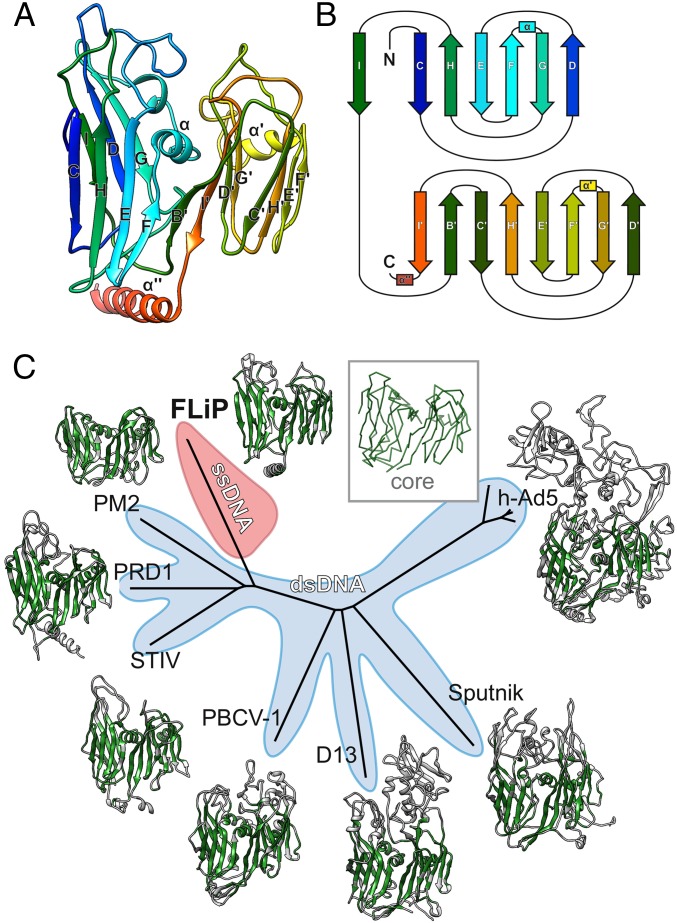
Fig. 3.
FLiP MCP fold and structure-based phylogeny. (A) The structure of the FLiP MCP is shown as a ribbon representation, colored from the N terminus (blue) to the C terminus (red). The β-strands in the N-terminal β-barrel are labeled C–I, and the β-strands in the C-terminal β-barrel are labeled B′–I′. α-Helices are labeled α, α′, and α′′. (B) A schematic diagram illustrating the topology of the double β-barrel jellyroll fold. The secondary structure elements are labeled and colored as in A. C, C terminus; N, N terminus. (C) Structure-based phylogenetic tree derived from alignment of MCPs (30) from FLiP, bacteriophage PM2 (PDB code: 2WOC), bacteriophage PRD1 (PDB ID code: 1HX6), Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus (STIV; PDB ID code: 2BBD), Paramecium bursaria chlorella virus 1 (PBCV-1; PDB ID code: 1M3Y), Vaccinia virus Western Reserve D13 (D13; PDB ID code: 2YGB), Sputnik virophage (PDB ID code: 3J26), and human adenovirus 5 (h-Ad5; PDB ID code 1P30). The region of each protein used in the structure-based alignment is colored in green. A generalized common core of the fold is shown as a C-αtrace in the Inset. Branches corresponding to viruses with dsDNA genomes are shaded light blue. The branch corresponding to FLiP, the only characterized member the lineage with an ssDNA genome, is highlighted in red.