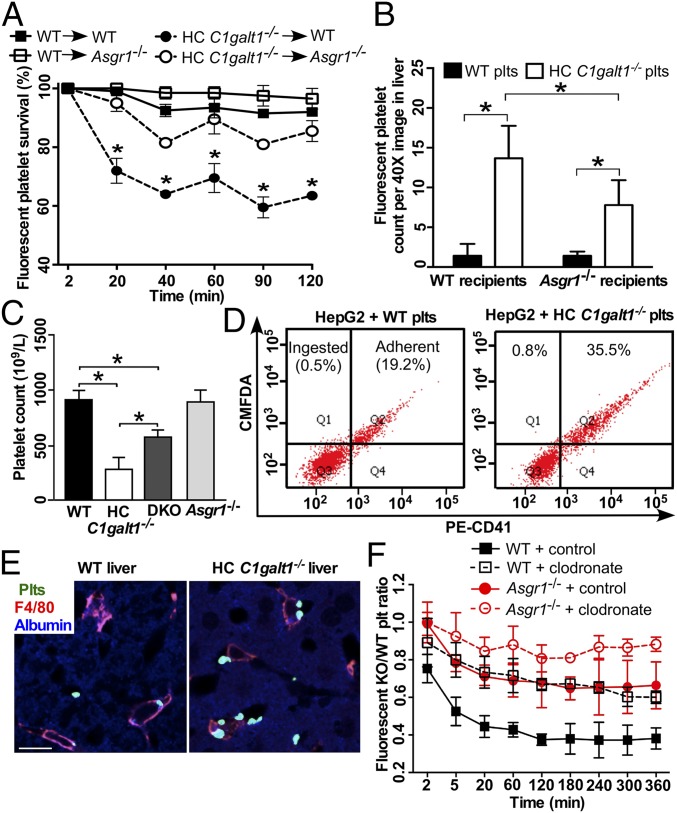
Fig. 2.
The AMR participates in HC C1galt1−/− platelet clearance. (A) Survival percentage of competitively transfused CMRA-labeled WT platelets or CMFDA-labeled HC C1galt1−/− platelets in peripheral blood of either WT or Asgr1−/− recipients. n = 3 experiments. *P < 0.05. (B) Quantification of labeled WT or HC C1galt1−/− platelets in recipient liver sections. Data are mean ± SD. n equals at least five randomly selected 40× microscopic fields. *P < 0.05. (C) Peripheral platelet count of WT and HC C1galt1−/−;Asgr1−/− mice. n = 3 mice/genotype. *P < 0.05. (D) Flow-cytometric analysis of HepG2 cell ingestion of CMFDA-labeled platelets. Platelet adherent to HepG2 cells were identified as CD41 and CMFDA double positive. CMFDA single-positive HepG2 cells suggest ingestion of platelets. The dot plots are representative of five experiments. (E) Representative images of immunostaining of platelets (anti-thrombocyte serum, green), Kupffer cells (F4/80, red), and hepatocytes (albumin, blue) in liver sections. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (F) The ratio of competitively transfused fluorescent HC C1galt1−/− platelets to WT platelets in peripheral blood of WT and Asgr1−/− recipients with or without Kupffer cell depletion. Data are mean ± SD at each time point. n = 6 mice per group.