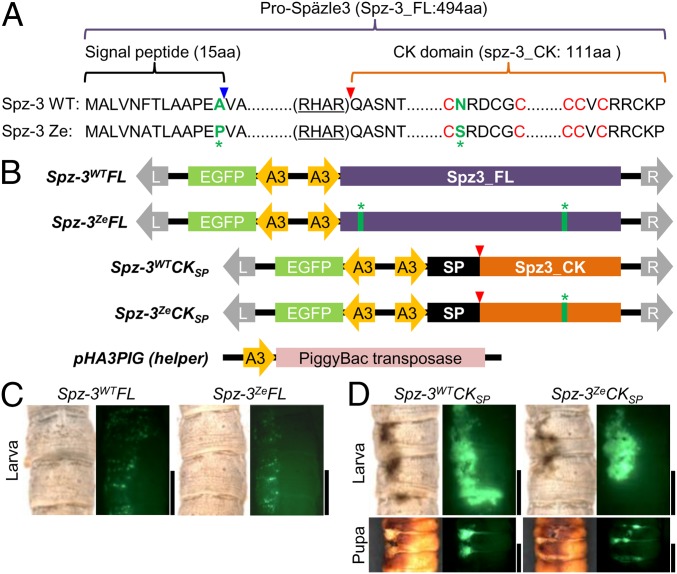
Fig. 3.
Ectopic expression of transgene Bmspz-3 causes melanin pigmentation of the larval and pupal cuticle. (A) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of Spz-3 of the Ze and WT strains. Green letters indicate nonsynonymous substitutions, and red letters C indicate highly conserved cysteine motifs among the spz family genes. (B) Scheme of plasmids for transgenic ectopic expression of Bmspz-3 and the helper plasmid pHA3PIG, which encodes piggyBac transposase. All plasmids contained the A3 promoter of Bmactin3, EGFP as a reporter, and recognition sequences of piggyBac (L and R with gray arrows). We prepared plasmids, which encoded the full-length ORF of Bmspz-3 (Spz-3WTFL and Spz-3ZeFL for WT and Ze, respectively), and the CK domain region, where the processed form functioned with the signal peptide (26) (Spz-3WTCKSP and Spz-3ZeCKSP) of both of the Ze and WT strains, respectively, to test whether melanin pigmentation was caused by Bmspz-3. The blue and red arrowheads in A and B indicate processing sites for the signal peptide and the processed form of Bmspz-3, respectively. The green asterisks indicate the sites of nonsynonymous substitutions as in A. (C and D) The phenotypes of ectopic expression of the full-length (C) and processed (D) forms of Bmspz-3 in larvae and pupa are shown, respectively. (Scale bars: 5 mm.)