Figure 2.
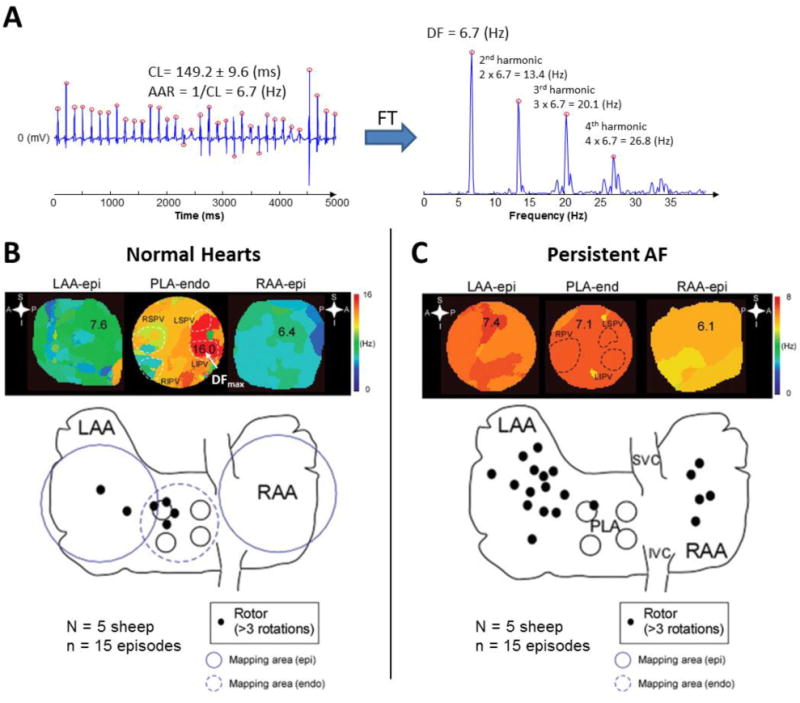
A. Bipolar electrogram obtained from the left atrial appendage of a patient with AF. Red circles display activation times. CL: cycle length, AAR: average activation rate, FT: Fourier Transform, DF: Dominant Frequency. Note that the fundamental peak of the spectrum is located at a frequency (DF) that matches the AAR. The peaks located at the frequencies multiple of the DF are called harmonics. A harmonic peak should not be selected as DF since this would lead to wrong conclusions. B. Top: DF maps in a normal sheep heart during stretch-induced AF showing fibrillatory conduction from the highest frequency domain (DFmax, 16 Hz, in red) located at the PLA, specifically at the LSPV and LIPV. Colors in each map indicate atrial areas (domains) with different DFs. The color bar on the right indicates frequency in Hz. A large frequency gradient between the fastest (red) and the slowest (blue) domains is usually found in acute episodes of AF. Bottom: Aggregated data from normal sheep hearts during stretch-induced AF showed that rotors were mainly located at the PLA and LAA. C. Top: DF maps of atria from sheep with persistent AF where a more homogeneous distribution of DFs (lower gradient) was found. The DFmax domain was located at the LAA (in red, 7.4 Hz). Colors in each map indicate atrial areas (domains) with different DFs. The color bar on the right indicates frequency in Hz. As shown, in persistent AF, the frequency gradient between the fastest and the slowest domains is usually smaller than in paroxysmal episodes. Bottom: Aggregated data from hearts showed that, in persistent AF, the role of the pulmonary veins becomes less prevalent in terms of harboring rotors. Endo: endocardial view, Epi: epicardial view, LAA: left atrial appendage, LIPV: left inferior pulmonary vein, LSPV: left superior pulmonary vein, PLA: posterior left atrium, RAA: right atrial appendage, RIPV: right inferior pulmonary vein, RPV: right pulmonary vein (B and C adapted from Yamazaki et al.28 by permission of Oxford University Press).
